HW Community
Lahaul-Spiti: Haughty Minister Allegedly Heckling Tribal Women Who Dared to Deny Him Entry in District Over Quarantine Violation
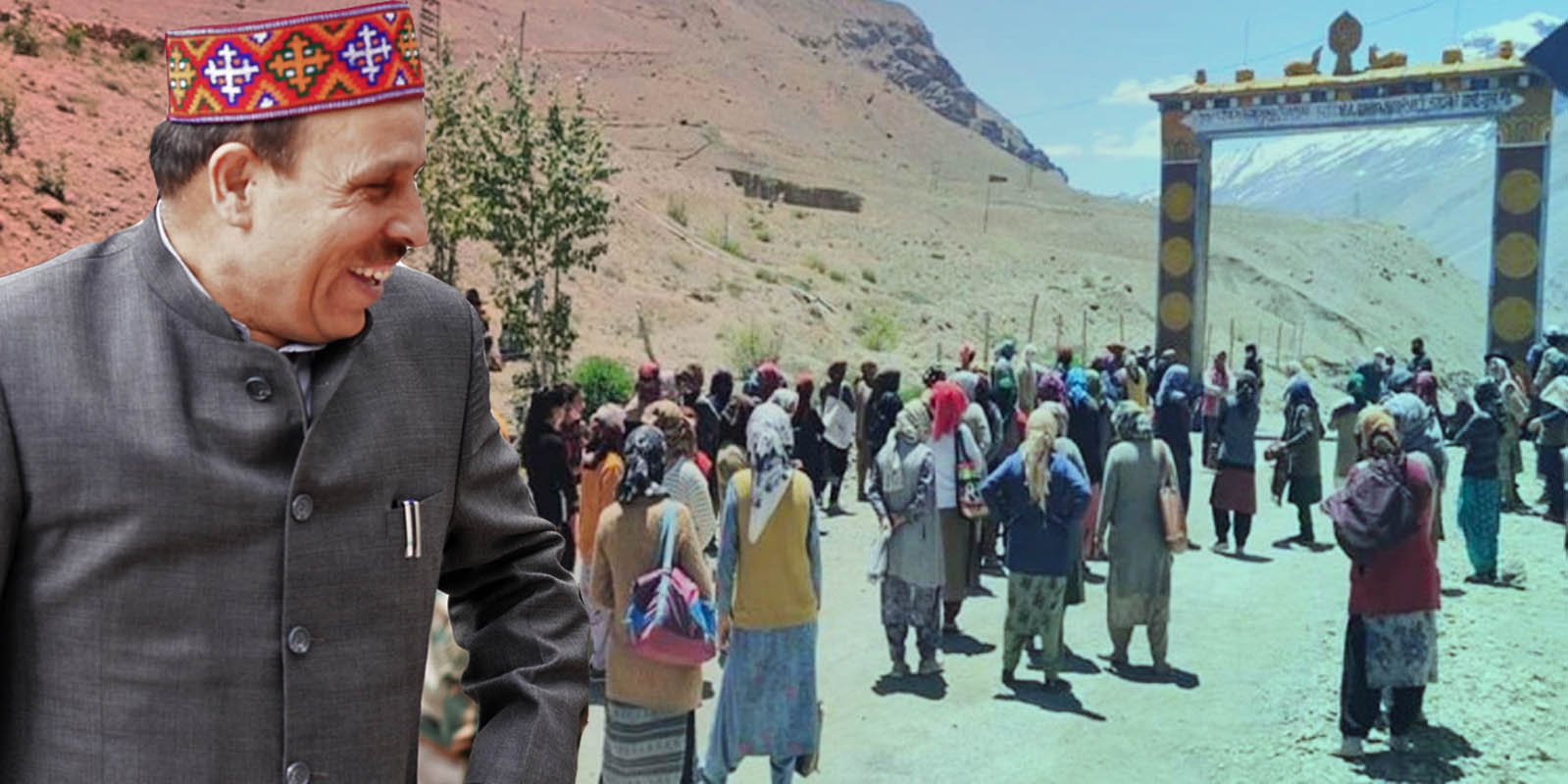

Lahaul-Spiti-Support is pouring in for the tribal women of Spiti after the local administration initiated police action against nearly 200 women for protesting against Himachal Pradesh Agriculture Minister Ram Lal Markanda for violating the local quarantine rules early in June. Locals said earlier only some specific protestors were being identified and booked. In response to this embarrassment, Markanda tried to give it a political color by alleging that oppositions had conspired this protest. So all women from each household gave a list of their names to the police identifying themselves as protestors. Following which these women were booked.
On June 9, hundreds of representatives of Mahila Mandals apart from some youth and other residents including employees of the State Government from Spiti carried out an agitation to protest the violation of the ongoing self-imposed lockdown in the region amidst apprehensions of the spread of Corona pandemic in the region.
The women had gathered at the gate in Kaza and did not allow Markanda and his convey of over a dozen of vehicles to enter district without following community rule regarding mandatory quarantine.
They wanted Markanda and his cavalcade to follow the rule like everyone else. Markanda did not agree to it and had to return to Shimla following this demonstration. However, instead of respecting the decision of the locals, now he is after the protestors. The ego of the haughty minister seems to be so big that the police was made to book a woman in almost every family in Kaza. This action is highly unacceptable if democratic values are considered. He forgot that he is supposed to respect the mandate of the people who had elected him. Instead, as alleged by the women, he wants a written apology.
More than 190 women were booked under Sections 341 (wrongful restraint), 143 (unlawful assembly) and 188 (disobedience of public order) of the IPC. These charges also include not maintaining social distancing while protesting. Markanda said he believed that the women were politically motivated, and now, as it appears, he is trying to set an example to discourage such dissent in the future.
However, as a matter of fact, Lahaul-Spiti had managed to remain COVID-19 free until June 30 – the day first two cases were reported in migrant labourers working for the BRO. Spiti has still not reported even a single case. It was due to the initiative and proactiveness of the locals who had framed their own rule regarding entry and quarantine. All residents of the region had agreed to follow the same also asked everyone to adhere to these rules.
“We have been following our COVID-19 rules as framed by our local committee, comprising members from local monasteries and community leaders, much before the state framed the rules. Our rules are applicable to all people, including our family members, who are returning to the area for the first time since the pandemic,”
Mahila Mandal President Sonam Dolma told news agency IANS.
The COVID-19 tally has crossed 1000 mark in the State but Lahaul-Spiti district is still doing far better than others with only four cases till July 2.
Instead of filing cases against them, these residents deserved to be appreciated for preventing infection entering into the district at a time when most of the other districts were reporting COVID-19 cases. The display of unity and understanding of democracy by these tribal women is outstanding. Rest of India should learn from these tribal people.
Support Pours in For Tribal Women
These women are receiving support from other organizations and activists.
In this row, close to 20 women, representatives of various organizations, women’s groups, as well as, concerned individuals from across Himachal recently issued a joint solidarity statement in support of these women.
The statement said that the residents have highlighted that even before the imposition of the lockdown there was serious concern amongst the tribal community of Spiti about the pandemic given its remote geographical location and socio-economic vulnerabilities.
Given the tribal lifestyles and dependence on each other for their livelihoods, social distancing within the community was close to impossible. The absence of public health facilities would have meant that any spread of COVID would have unleashed a threat to the very existence of this tribal community, the representatives said in the statement issued.
The representatives said that in this scenario for the last four months, the local people, especially the Mahila Mandals, have worked relentlessly to facilitate quarantine of residents returning from outside, making masks and also guarding against people from outside the region visiting the region. The local committees had resolved that each and every person entering from outside would have to observe 15 days quarantine.
It needs to be noted that the women were already agitated by the continued pressure of some members of the Tribal Advisory Council to bring laborers from outside to the area, the representatives said.
“Despite being well aware of this context, the local administration instead of attempting a dialogue with the protestors has initiated police action against women who were simply asking that the local resolutions be duly followed and respected”,
said Ratan Manjari, leader of Mahila Kalyan Parishad, Kinnaur
The representatives said that the women have made it amply clear that they had no political motives and neither anything personal against the Minister. The representatives alleged that not only summons were issued selectively against some women representatives of Mahila Mandals but they are also being heckled to issue an apology and harassed by the administration daily.
The representatives alleged that some departments have also issued show-cause notices to their local women staff who participated in the protest. Apparently, cases have been registered under IPC sections 341,143 and 188.
“We condemn this harassment of the tribal women by police and the local administration. Whereas across the state legal action was initiated against those violating the lockdown, when local people made the demand that lockdown rules be followed in their area, the police has, in turn, initiated action against them. This reflects the double standards, high-handedness and patriarchal nature of the government agencies and the State. We also believe that this unjustified action of the police is to create fear amongst the local community”
said Himshi Singh of Himdhara Collective Notably, Spiti is a schedule V area and the constitution empowers the communities for self-governance.
Further, the women of the region seem to be well aware that if there is a COVID outbreak then they, who already bear the burden of care and nurturing work in the family and community, will be burdened even further, the representatives said.
“It is rather unfortunate that women are expected to be present to welcome political representatives but when they have a genuine issue to raise about the actions of the same representatives they are silenced and repressed. In such a scenario how will women even be considered equal citizens of our democracy?”
said Vimla Vishwapremi of Parvatiya Mahila Adhikar Manch.
The open statement has demanded that the charges against the tribal women of Spiti be dropped and that their harassment and repression by the local administration be immediately stopped. The local administration must acknowledge and support the participation and leadership of the local tribal community, specifically the Mahila Mandals, and work together to maintain the safety and security of the region, the representatives said in the joint statement.
HW Community
PIL Filed in HP High Court Re-Ignites Quest for Recognizing Pahari (Himachali) as Hill State’s Official Language
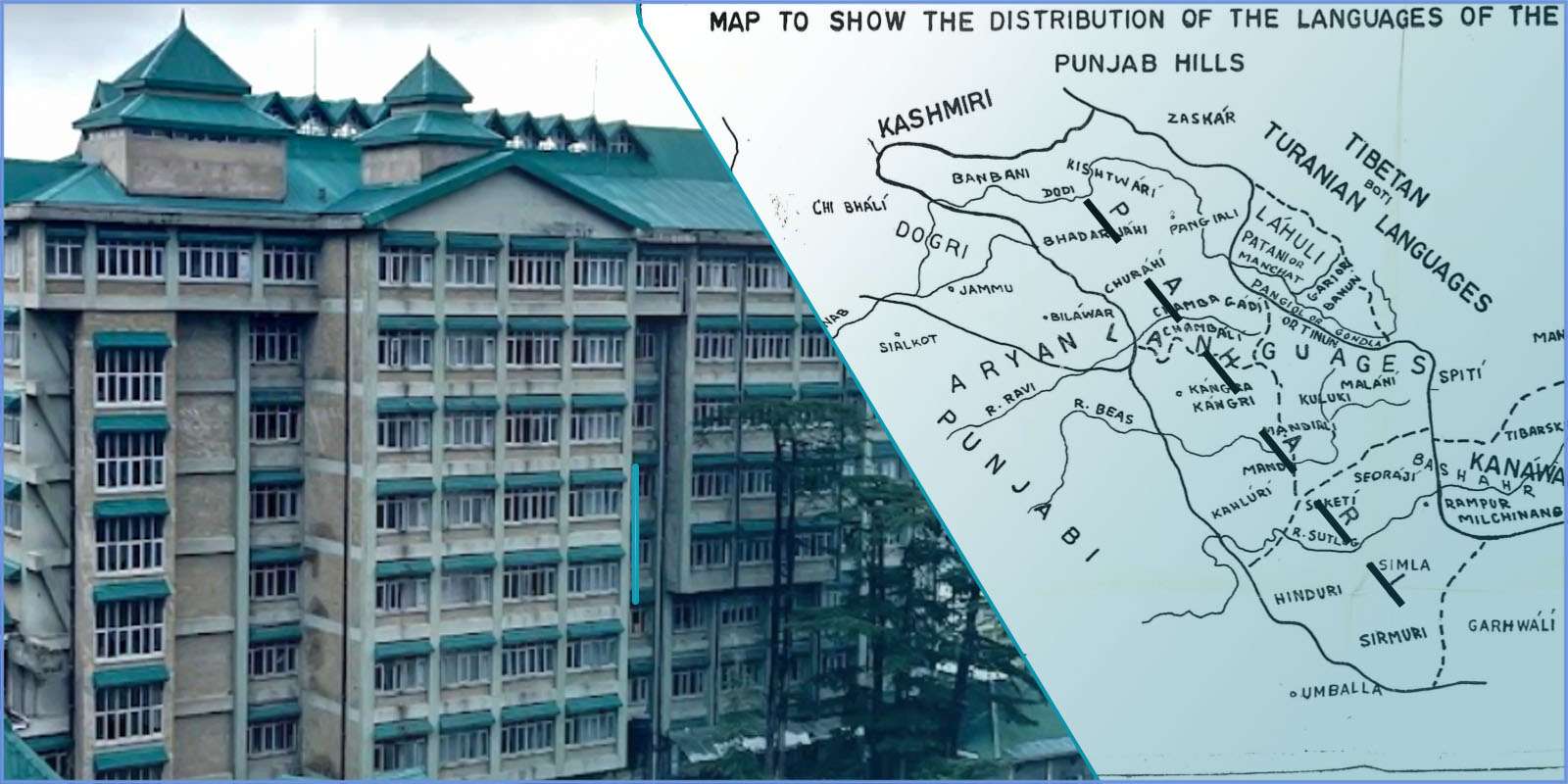

Shimla- November 10, 2021, Himachal Pradesh High Court on Monday passed an order concerning a public interest litigation (PIL) seeking to recognize Pahari (Himachali) as an official language of the state. The petition also sought effective steps on the part of the government to preserve and promote the Pahari language in the State as its culture and language give it a distinct identity.
The Public Interest Litigation was filed by Arsh Dhanotia with a prayer that the state be directed to declare Pahari (Himachali) as one of the official languages in the State of Himachal Pradesh in any script and also promote further research towards a long-term formal Pahari (Himachali) nuclear language structure and nuclear Tankri script.
Bhawani Pratap Singh Kutlahria, the advocate for the petitioner, argued in the court that the State Government be directed to promote Pahari (Himachali) and other local languages as the medium of instruction in primary and middle-level schools as per the New Education Policy, 2020. On behalf of the petitioner, he also prayed the court to direct the state government to include Pahari (Himachali) language as a separate category for the 2021 Census and simultaneously undertake an awareness campaign to create awareness amongst the masses, especially the youth of the State who speak Pahari (Himachali), to get it marked as their mother tongue in the upcoming Census.
A bench of Chief Justice Mohammad Rafiq and Justice Sabina while disposing off the PIL stated,
“The direction as has been prayed for, cannot be issued to the State Government until and unless it is established on record that the Pahari (Himachali) language has its own script and that a common Pahari dialect is spoken throughout the State of Himachal Pradesh. We, however, set the petitioner at liberty to approach the Department of Language Art & Culture to the Government of Himachal Pradesh with his demand for undertaking research to promote a common Pahari (Himachali) nuclear language structure and nuclear Tankri script. If the petitioner approaches the respondents-State through its Additional Chief Secretary (Language Art & Culture) to the Government of Himachal Pradesh) for the prayer made in the Civil Writ Public Interest Litigation, it would be for the said authority to consider the same in accordance with the law.”
Additionally, the petition had emphasised that Sanskrit, which is the second official language of the state, had only 936 speakers according to the 2011 census and Pahari (Himachali) dialect chain which is spoken by more than 40 lakh people was being neglected and has not been made an official language even after having so many speakers.
The petition also highlighted works of Former Chief Minister Late YS Parmar and Former Education Minister Late Narain Chand Parashar towards the promotion of the Pahari (Himachali) language.
What’s Pahari (Himachali) Language, How Many Districts It Covers
It is to be noted that according to the petitioner, Pahari (Himachali) is a combined term used for the Western Pahari dialect chain spoken in Himachal Pradesh and majorly includes Kangri, Mandeali, Chambeali, Kulvi, Mahasu Pahari and Sirmauri. According to him ever since the creation of Himachal Pradesh, there has been a demand for recognition of Pahari (Himachali) under the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and it is also officially listed with 37 more languages as a language which is in significant demand to be included in the scheduled languages category.
In his plea, he also stated that the Himachal Pradesh Vidhan Sabha in 1970 and 2010 have also passed resolutions concerning the promotion and development of Pahari (Himachali).
Environment
Himachal’s Snow Covered Area Has Decreased, Poses Big Threat to State Economy’s Lifelines: Report
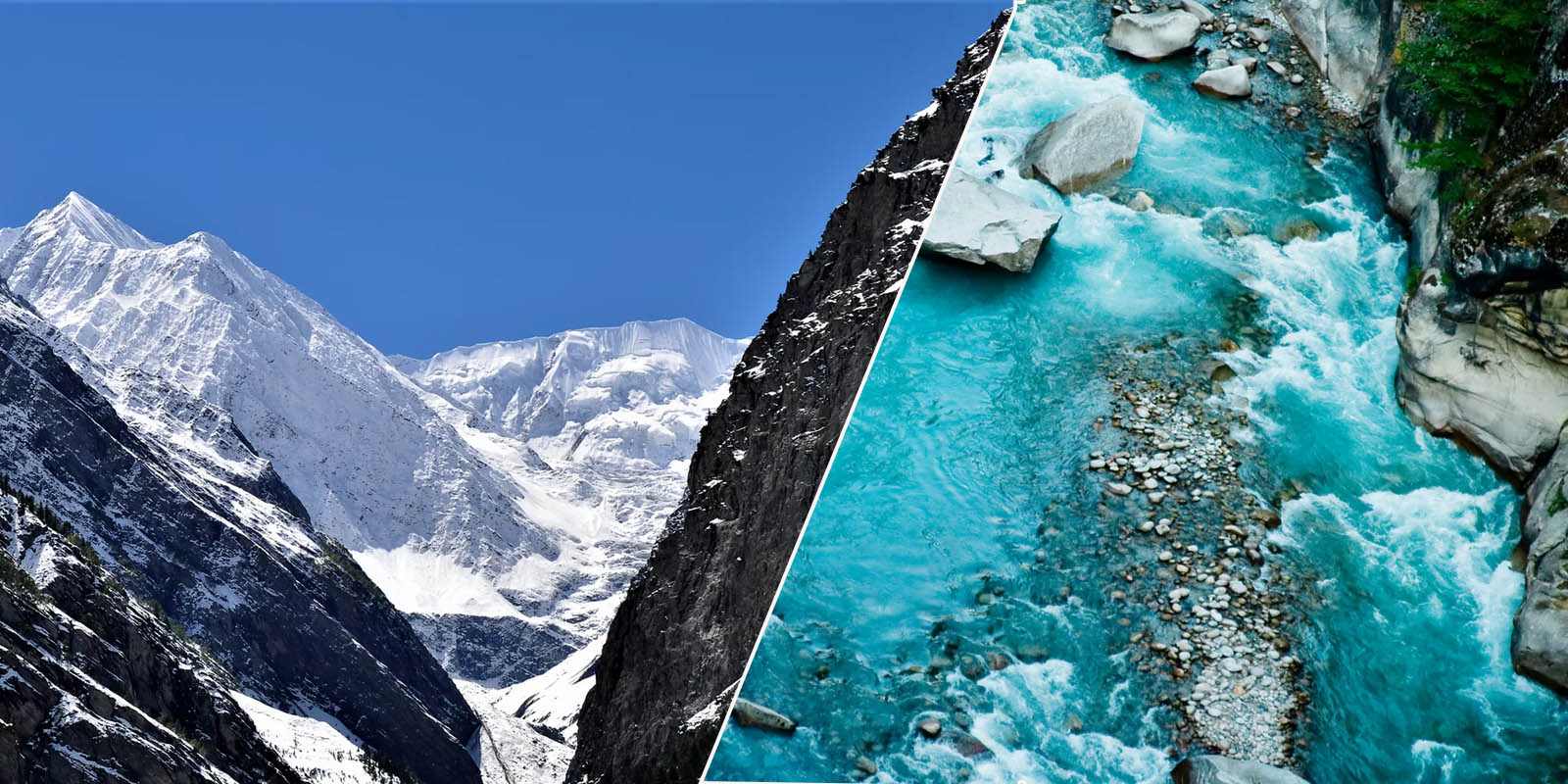

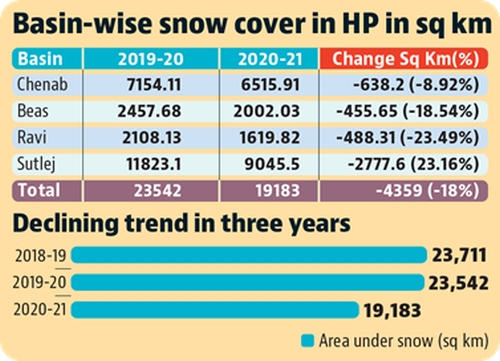
Shimla-The area under snow cover in Himachal Pradesh has declined by 18.5% according to a recent report published by State Centre on Climate Change (SCCC) and Space Application Center (ISRO) Ahmedabad. The report revealed this decreasing trend for the five major river basins in the State.
As the report points out, the high altitude regions of Himachal Pradesh receive precipitation mainly in the form of snow during the winter season. One-third of the geographical area of the state is covered by a thick blanket of snow during the winter season. Rivers like Chenab, Beas, Parvati, Baspa, Spiti, Ravi, Sutlej and its tributaries flowing through Himachal are dependent on snowfall in winter. These rivers mainly feed into the Indus water system and a decline at this rate rings a death knell for water and also food security for millions of people from Himachal to Kashmir, the plains of Punjab, the food bowl of the country.
Using images and data received from satellites, the report states, that the winter precipitation was mapped in all the basins from October 2020 to May 2021 (a period of two years). The findings indicate that there has been an average decrease of 8.92 percent in Chenab basin, 18.54 percent in Beas basin, 23.16 percent in Ravi basin, 23.49 percent in Sutlej basin compared to last year. The ice covered area of Chenab basin was 7154.11 sq km in 2019-20, which has come down to 6515.91 sq km in 2020-21. Similarly, Beas basin was reduced from 2457.68 to 2002.03 square kilometer, Ravi basin from 2108.13 square kilometer to 1619.82 square kilometer and Sutlej from 11823.1 square kilometer to 9045 square kilometers. Overall, the snow covered area was reduced from 23542 square kilometer to 19183 square kilometer in the entire Himachal.
Sutlej Basin covers 45 per cent of the total geographical area of Himachal and it is the longest river of the state. It flows for around 320 kms here, passing through Lahaul and Spiti, Kinnaur, Shimla, Kullu, Mandi, Solan and Bilaspur districts, along its course. The above study shows that the maximum reduction in snow cover has occurred in the Sutlej basin. An area of 4359 square kilometers under snow cover has decreased for the whole state, of which more than half of the Sutlej Basin.
Just two years ago another study had indicated that more than half of glaciers in Sutlej Basin are set to vanish by 2050. Yet another study also showed that the Sutlej basin has the highest 562 number of glacial lakes. These lakes stand the risk of sudden outbursts, which then causes flash floods downstream as the valley has already experienced. So, while the crisis that is unfolding, be it deglaciation, lake formation or reduction in area under snow cover, it seems that the Sutlej river basin is more vulnerable to these changes.
Prakash Bhandari, an environmental researcher and activist and member of Himdhara Collective expressing his concern states that the situation in the Sutlej river basin is certainly indicative of a serious climate emergency and it is critical to look into the drivers of this both local and global.
“The Sutlej basin catchment is the largest and so the changes visible here are more significant. Many factors have worked together to create this crisis which should be studied closely. There is no doubt that global warming is contributing to these changes. But the local conditions also play a role in reducing or increasing its impact”, he says.
The upper reaches of the Sutlej Valley, especially areas like Kinnaur are geologically fragile, with sharp gradients and loose soil strata. Vegetation is in a very small area so the proneness to erosion. We have seen the catastrophic impacts of flashfloods and landslides over the last decade and a half, where crores worth of property has been damaged. This year saw a spate of landslides where lives were lost. “In such a sensitive and also strategically important area, changes in the landscape will have far reaching and irreversible impacts. More construction activities will lead to more deforestation, more erosion”.
Construction of dams has been rampant in the Sutlej valley, a phenomena that started post independence and continues today. If all of the planned dams are built the Sutlej will be cho-a-cloc with more then 150, large and small projects. At the bottom of the valley in Bilaspur is the Bhakra Dam, built almost 6 decades ago, which has a size of 168 sq km and a storage capacity of 9.340 cubic km. Is. This is followed by the Kol Dam which extends for 42 km up to Sunni, which has a total storage capacity of 90 million cubic metres. Nathpa Jhakri Project which is 27.394 kms. is long. When a dam is built, a huge amount of water is stored. The debris of many villages, trees etc. also gets absorbed inside the dam. When water is stagnant, it receives heat from the Sun to form mist in the surrounding area by evaporation and simultaneously generates methane gas. The experience of the lake formed by the Kol dam at Tattapani in Mandi district shows that the area is experiencing heavy haze which was not there earlier.
“In the 30s and 40s, Shikari Devi and Kamrunag used to have snow on the peaks for about 6 months, which now could barely stop for only 2 months. The air route distance of Shikari Devi and Kamrunag is only 26 to 30 kms from Tattapani lake. At the same time, their distance is not much from the cement factories of Darlaghat, Sundernagar”, the elders in the area say. “Today, fog is prevalent and this has also made the area warmer”.
Due to the warming of the weather due to the clouds formed from the mist, the snow has started melting quickly. Apart from this the local crop patterns are affected. Post the 1990s, the Sutlej became a site for run of the river hydroelectric projects using extensive underground tunneling. This involves massive use of explosives for blasting through the mountains. Of the 23,000 MW worth of projects to be constructed in Himachal more than 10,000, a third are from this valley alone. Kinnaur continues to be a hydel powerhouse with 10 run of the river projects in progress and 30 more to be set up including two mega projects of 1500 MW and 1000 MW each. This paints a scary picture.
Interactive Sutlej River-Basin Map indicate Hydropower Station location
It is not just the hydro-electric dams but unplanned tourism and other development activities like mining, cement plants, road expansion and mindless construction across the high Himalayan regions have also add to the shift in local weather patterns, land use changes and thus the ecological crisis. But the reason why we should put the limelight on hydropower is that this is being pushed as “Green Energy”, in the name of climate change mitigation. As opposed to other forms of generating power, hydropower projects are said to cause lesser carbon emissions, which is why there has been a global push to shift to renewable resources. But the climate emergency in the Himalayas has put a question mark on ‘water’ as a renewable resource.
The question then arises that with all this data indicating a steady decline in river discharge and snow cover have our planners and policy makers not considered what will happen to these projects? Will they be able to generate the power they propose to? The people of Himalaya have to wake up to this wastage of public resources. Scarce funds should be diverted to better planning for securing local livelihoods by protecting the forest ecosystems and water sources for the future.
Author: Gagandeep Singh-From Himdhara (Environment Research and Action Collective)
Feature Images: unsplash/@raimondklavins
HW Community
Himachal: Warnings of Delta Plus Virulence Fall on Deaf Ears, No Restriction on Visitors from Affected States

Shimla-Yesterday, the Centre government directed the state governments to take immediate measure in wake of the spread of more infectious Delta Plus variant. As the Delta Plus variant is posing a threat of the third wave, the states were told to take steps like preventing crowds, increase testing, more focus on surveillance, contact tracing and put boosting vaccine coverage on a priority basis. Following it, Himachal Pradesh Government might have announced an alert over Delta plus variant, but there wasn’t any follow up on instructions passed by scientists and health experts to take strict restrictive measures ahead of the impending third wave.
To make it worse, high rank officials and political leaders were seen flouting Covid-19 SOPs on several occasion, which sent wrong messages to the masses. The pictures and videos showing flouting of Covid appropriate behavior by Chief Minister Jairam Thakur and Directorial General of Police, Sanjay Kundu, alongwith other staff for Anupam Kher is the most recent to mention. A group photograph and video of the same were widely circulated on social media and invited huge criticism from the people.
So far, the state has not reported any case of the Delta Plus variant. But the neighboring states – Punjab, Haryana, and Jammu & Kashmir – reported their first cases yesterday. This puts the boarding areas, like in Una district, at a higher risk. Chief Secretary to HP Government, Anil Khachi, yesterday said samples have been sent for genome sequencing.
Despite repeated warnings of Delta plus variant (B.1.617.2.1.), Himachal Pradesh has thrown its borders open to all and lifted all restrictions for inter-state travel in just one go. From June 23 onwards, the state government removed the condition for registering on the e-pass portal for visitors intending to enter the state. In the Cabinet meeting held on June 22, 201, the government first decided that e-pass restrictions would be removed from July 1, but later it changed the decision and instead implemented it immediately.
This haphazard decision is said to have come under huge pressure from the hospitality industry – the worst-hit sector, leading to financial crisis and mass unemployment among its stakeholders. Related associations had been approaching Chief Minister Jairam Thakur with their pleas to provide relief, but mostly faced disappointment. The stakeholders say the state government didn’t provide any significant relief, which is making the survival of the industry difficult.
Also Read: Read Eight Reliefs That Himachal’s Devastated Tourism Industry Seeks from HP Govt
Also, stakeholder of the industry, especially hoteliers, had been demanding the removal of restrictions and conditions on the entry of tourists to Himachal so that they could fetch the remaining peak tourist season.
With its inability to offer relief, the HP Government took the chance to waive off restrictions in a haste.
At the same time, the state government has decided to conduct offline examinations for the undergraduate classes starting from July. A section of the students had been condemning the HP government for scheduling exams without vaccinating students. Some student bodies had been asking the government as to why online classes were possible but not online exams.
The state government also waived off restrictions on timings for the opening of markets/shops.
As scientists and health experts warn of the virulence of the new variant and with neighboring states already on alert after reporting cases of the new variant, the HP government hasn’t even mentioned any intention to at least put a check on the visitor from the states where cases of Delta Plus are being reported. Carrying an RT-PCR negative report for visitors from such states/cities would have been a wiser step.
Officially, the state is on alert, but no measures have been announced to check the entry and spread of the variant into the state. The state government does speak of preparing for the anticipated third wave, but there is hardly any long-term preventive strategy. The Covid appropriate behavior is hard to adopt when markets and tourist places are crowded with visitors.
Why Delta Plus is a Big Concern
The World Health Organization (WHO) has labelled the Delta variant as ‘Variant of Concern’.
The Centre and scientific/medical institutes in India also agree with that Delta Plus as a variant of concern and could be the cause of impending third wave. Last Tuesday, based on the findings of INSACOG, the Union Health Ministry had alerted and advised Maharashtra, Kerala and Madhya Pradesh regarding the Delta Plus variant of COVID19.
INSACOG had warned that the Delta Plus variant has increased transmissibility, stronger binding to receptors of lung cells, potential reduction in monoclonal antibody response.
“Delta variant is more resistant to medication, treatment and vaccination. Therefore, people who have been vaccinated can still be affected by this variant and can go on to get a clinical illness, Archana Dhawan Bajaj, director, Nurture IVF, told a national English Daily.
“Neutralising antibodies against this variant post-vaccination seem to be nearly five times lower in people who have already been vaccinated than the other variants,” she said.
Further, Dr Raman Gangakhedkar, ex-Head Scientist of Epidemiology and communicable diseases, ICMR, has also expressed concern over the reports that Delta Plus has reported pathophysiologic change and affecting different organs. Dr Raman says that it could transfer from cell to cell and would more likely produce neurological symptoms as a common manifestation.
So far India has reported 51 cases of the Delta Plus variant.
Delta Plus variant is a variant of Delta with an additional mutation -B.1.617.2.1.














 Home Decor Ideas 2020
Home Decor Ideas 2020