HW Community
Here is What CM Jairam and MLA Dhawala Said While Proposing Legalization of Cannabis (Hemp) Cultivation in Himachal

Shimla-As usual, while the Budget presented by the Himachal Pradesh Government for the 2021-22 financial year is being hailed by legislators and leaders of Bharatiya Janata Party, the oppositions are terming it an eye-wash and a directionless budget. As usual, the budget speech contains a plethora of promises including filling up about 30,000 functional posts and constructing 12,000 news houses for the poor.
However, there is one proposal that deserves appreciation in particular. Not only it would open more doors of employment in rural areas, but could also prove to be a crucial decision in revolutionizing the state economy. A potential source of income that remained untapped.
It’s about permitting commercial hemp cultivation in the state. In his budget speech, Chief Minister Jairam Thakur told the House that the State Government would frame a policy to legalize hemp cultivation.
“Commercial hemp cultivation is permitted & regulated in many countries and in some States in India. This creates investment and employment opportunities. State Government proposes to frame a policy to permit commercial hemp cultivation with the proper regulatory framework,” he said during his budget speech on March 6, 2021.
The State High Court had already given its nod and put the ball in State Government’s court by stating that it has no objection over permitting the cultivation of industrial and medicinal hemp. Himachal Watcher had covered the issue when it was in court.
It’s pertinent to mention here that Hemp is one of the varieties of Cannabis sativa, which cannot be used as a psychoactive substance to get high. In simple words, it would not get you high even if you try to do so by smoking it because it contains a negligible amount (.1%) of the psychoactive substance Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Also Read: Misconceptions keep Himachal from making fortune on ‘green gold’ and eradicate charas mafia
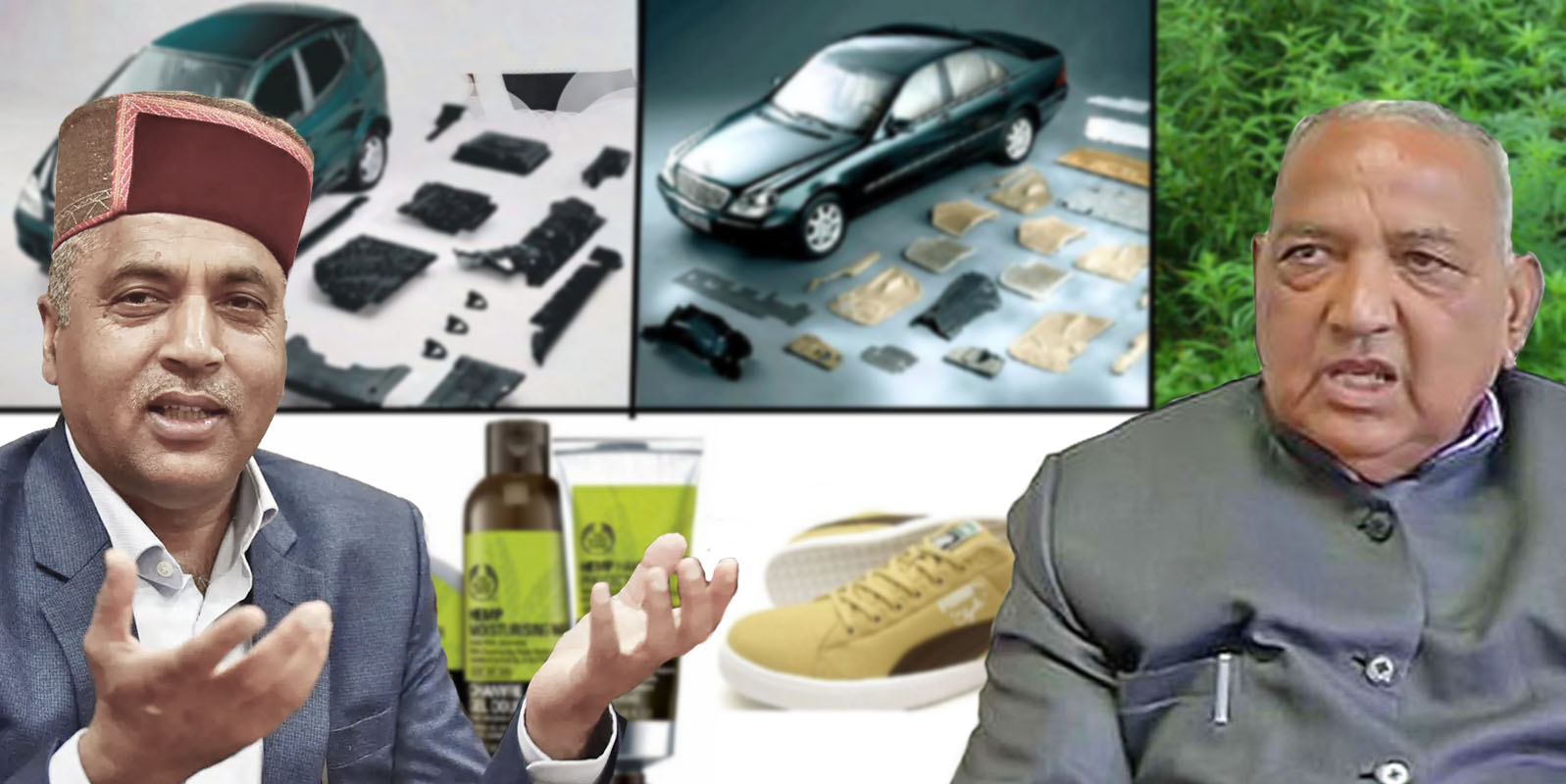
On March 5, 2021, Ramesh Chand Dhawala, MLA of Jawalamukhi constituency, introduced a resolution in the Budget Session proposing the legalization of the cultivation of hemp. He had argued over the benefits of doing so at a length. Chief Minister Jairam Thakur had also agreed that the state should frame a policy and undertake the cultivation of cannabis in a controlled manner. Chief Minister had also said that cannabis is has a strong association with the culture of the state. He admitted that traditionally fibre obtained from cannabis plants, which is known as “Shail” was used to make ropes, shoes and matts. He mentioned how extracting cannabis oil to use it in winters with food or as body lotion was common practice. Further, these seeds were used to be a part of the famous Himachali cuisine “Siddu”, he mentioned.
“American Cancer Research Association has found that cannabis is effective in slowing down the development of brain tumour and lung and breast cancer,” he said in the House.
Further, he mentioned that the Commission on Narcotic Drugs (CND) has remove cannabis from Schedule IV of the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs — where it was listed alongside specific deadly, addictive opioids, including heroin, recognized as having little to no therapeutic purposes.
Video
Dhawala, prior to Chief Minister’s reply, told the house that the NDPS Act was introduced to check substance abuse, not to prevent the manufacturing of clothes and medicine. Traditionally, the cannabis plant was used locally to create clothing. Currently, he said, 70-80 percent of prisoners are booked under the NDPS Act. Record cases under NDPS have come to light in Kullu and Chamba for the illegal cultivation of cannabis.
These include poor people who remain behind bars for decades as trials take a huge amount of time. The use of cannabis as a drug is rising among youth who are getting addicted to it. Legalizing hemp cultivation can solve this problem along with opening new doors for employment, he told the House.
In higher hills, the rural people can harness only one crop as the land remains covered in a thick blanket of snow for six months. Which pushes these people to get indulged in illegal cultivation of cannabis and paddling of smokable substances extracted from cannabis plants, like charas and hashish, for livelihood.
While those who are caught with a quantity more than 100 grams and kingpins must be acted upon, there are youngsters who are booked for possessing even small quantities, he said.
Further, emphasizing on commercial use of hemp, he told the house that a large number of goods that can be manufactured from hemp in addition to cannabis oil, which is in huge demand in the international market for its medicinal use, can bring fortunes to the state and the rural population deprived of any other sources of income.
Video
He referred to other states like Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand etc. where the governments have framed policies to permit the cultivation of commercial hemp. He said industries have been established which uses this cultivated hemp, especially its oil for the manufacture of medicines.
Further, not only goods like cloth, shoes, furniture, ropes etc. but bricks can be manufactured by using waste material. These bricks are highly durable when combined with lime. He said these bricks have more strength, are light-weight and are waterproof. In Island, Mark and Spencer’s company constructed its showroom completely using these bricks and world-renowned car manufactures like Ford are also using hemp for manufacturing of car accessories, he said.
Also Read: Two Himachal Youngsters to Launch State’s First Hemp Start-up: An Online Market for Green Products
Dhwala also said that legalizing hemp cultivation can also revolutionize the clothing industry. In India, mostly cotton is used in the clothing industry. Cultivation of cotton requires double the land and four times the water required for the cultivation of hemp. Also, hemp can be harnessed within three to four months as compared to cotton which takes about nine months, he said.
He also referred to the mention of cannabis as a medicine in Vedas. All parts of the cannabis plant – root, stem, leaves, fruit, seeds- are usable for various purposes. Ayurveda, in which cannabis is called ‘Vijaya’, also recommend the use of cannabis for cancer, neurological diseases, bacterial infection etc. and modern science also verify it, he said. The United States of America is using cannabis-based medicines for the treatment of diseases like Parkinson’s, Autism, Alzheimerinn ol, and others related to dementia. Other foreign countries are also using it as a medicine to treat heart-blockage, he told the House. Further, it is also used to provide relief to people suffering from disorders like migraine and stress.
Back in old days, cannabis oil was used as a pain reliever to mothers during delivery, he added.
The cannabis plant is the only plant that has up to 80 percent polyunsaturated fatty acids and a high quantity of nutrients Omega-3, Omega- and Omega-9. Other than cannabis, only fish contains these nutrients.
India’s neighbouring country Nepal has realized the potential of this plant and has formed a separate ministry that looks into the cultivation of hemp.
“It’s a matter of surprise that clothing, bags, shoes etc. made of hemp in Nepal are sold at high prices in Dharamshala, McLeodganj, and Manali,” he said.
Instead of wasting time and energy of the police force in uprooting cannabis plants and wasting them, the state government should permit its cultivation for industrial and medicinal use under Section 8, 10 and 14 of the NDPS Act, like it has been permitted in Uttarakhand, M.P, Orissa and some North Eastern States.
Scientists have confirmed that cannabis can be used for the treatment of cancer patients and to stimulate appetite in AIDS patients.
Clothing made of hemp fibre is known for its anti-bacterial features, which is why countries like Canada has patented undergarments made of hemp fibre, he said.
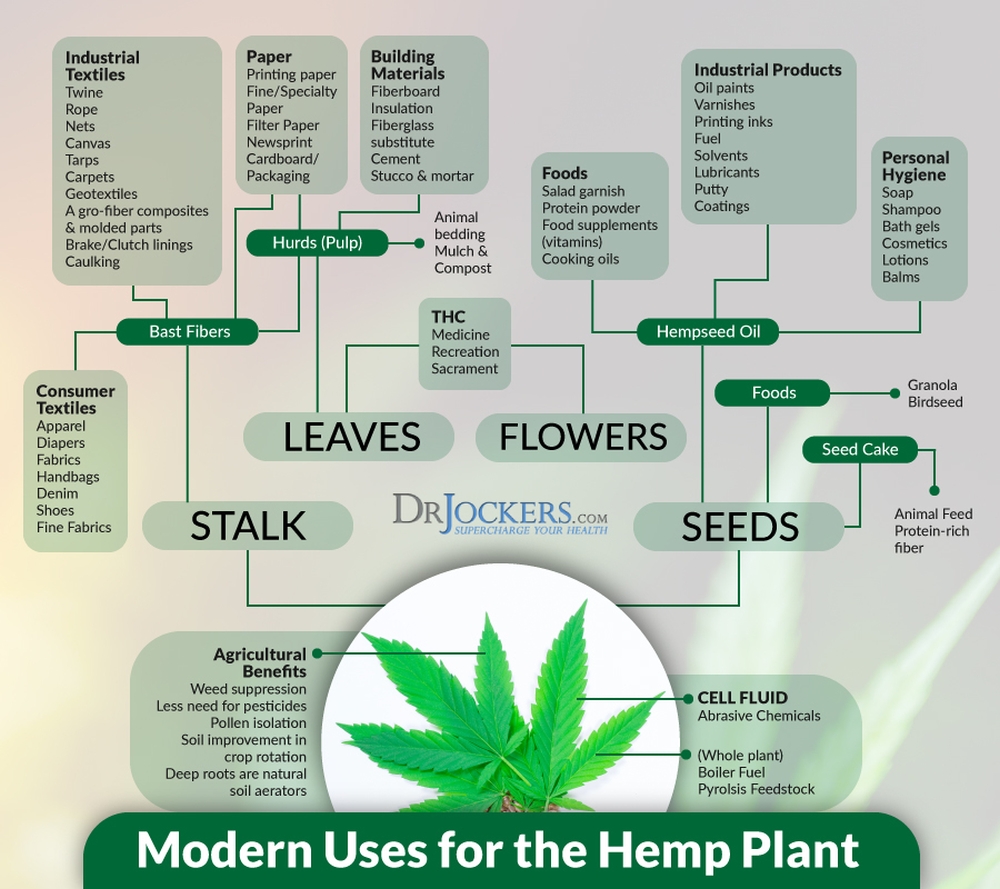
He further argued that currently, the wood used for the manufacture of furniture takes years before it’s ready for use, while a hemp plant takes only four to five months. Comparatively cheaper furniture could be prepared from this plant, which would not only offer an alternate source of income and employment but also prevent deforestation.
Though the United Nations had prohibited cannabis cultivation from 1985 onwards, in 2020, the same organization has lifted the restriction on its cultivation considering its immensely beneficial medicinal use, he told the House.
This plant is in high demand in the international pharmaceutical market and this demand is only growing.
The ban on cultivation relates to using cannabis as a psychoactive drug, which is only one of its 400 characteristics. There are two sub-species of cannabis – one which has a high amount of THC and others which have a negligible amount of THC (.3%), he said. In Uttarakhand, the type of plant which is being cultivated possess a negligible amount of THC and, thus, can’t be used as a psychoactive substance, he said.
Though Himachal Pradesh is known for apple production, the fact is that the cultivation of apple is limited to only Kullu, Shimla, Kinnaur, Bharmaur etc.
He also compared it to alcohol in terms of hazards.
“People die after consuming alcohol, but I never heard that anyone ever died after consuming cannabis, “he argued.
Citing another example to control the use of cannabis as a psychoactive substance, Dhawala said,
“People in a village that doesn’t have a legal liquor vendor start producing and selling home-made liquor. But if a legal liquor shop is allowed, it works as a deterrent for illegal production and sale.”
“Similarly, I believe that cultivation of cannabis should also be legalized so that not only people could get employment but also refrain from indulging in peddling, he said.
He also referred to the dependence of the State on debt taken from the Centre and said legalizing cannabis cultivation can help solve this problem.
“When the laws are more dangerous than the drug itself then a fight for civil liberties becomes necessary. Stopping research and knowledge is not only unconstitutional but a crime against evolution, Deven Khanna, a practising advocate at Himachal Pradesh and the man behind this initiative to transform the state’s economy.
Deven has been working with policymakers and arguing his petition to legalize the cultivation of industrial hemp in the State High Court for the last four years. It was on his petition that the court had given a go-ahead to the government. Not only the court, but Deven had also been collaborating with stakeholders in the hemp industry/villagers and doctors.
“The purpose of my petition was to open the market for non-narcotic/medical and industrial use of Hemp so that the locals have an alternative source of income, patients have access to safer natural medicines and for making available biodegradable /organic alternatives to plastic and construction material in the state,” Deven told Himachal Watcher.
“The foremost objective was empowerment and “creation of choice” for the local inhabitants who presently are being lured into illegal activities due to lack of avenues for making a decent livelihood. The only way to prevent people from doing illegal drug trade is sadly not deterrence which everyone is really fond of, its actually giving them an alternative choice to make a decent life,” he added.
“People are deterred by hunger more than jail. If this plant is used for non-narcotic purpose which generates money for the locals then there is a hope that they will choose the less risky and equally rewarding source of income rather than selling contraband,” Deven said.
“Right now, there is very little choice/opportunity in the villages and the drug mafia is solely controlling this plant. It’s appalling that drugs are easily available in society and medicines are not! What we seek is that the plant is rather put in the hands of our doctors, industrialists, food manufactures and not in the hands of the illegal drug market, he said.
“There are 100s of industries and youth startups who want to open hemp businesses in the State and with a billion-dollar industry the state can prosper a lot, this plant can do more for the people of the state than what apple did many years ago,” Deven said.
HW Community
PIL Filed in HP High Court Re-Ignites Quest for Recognizing Pahari (Himachali) as Hill State’s Official Language
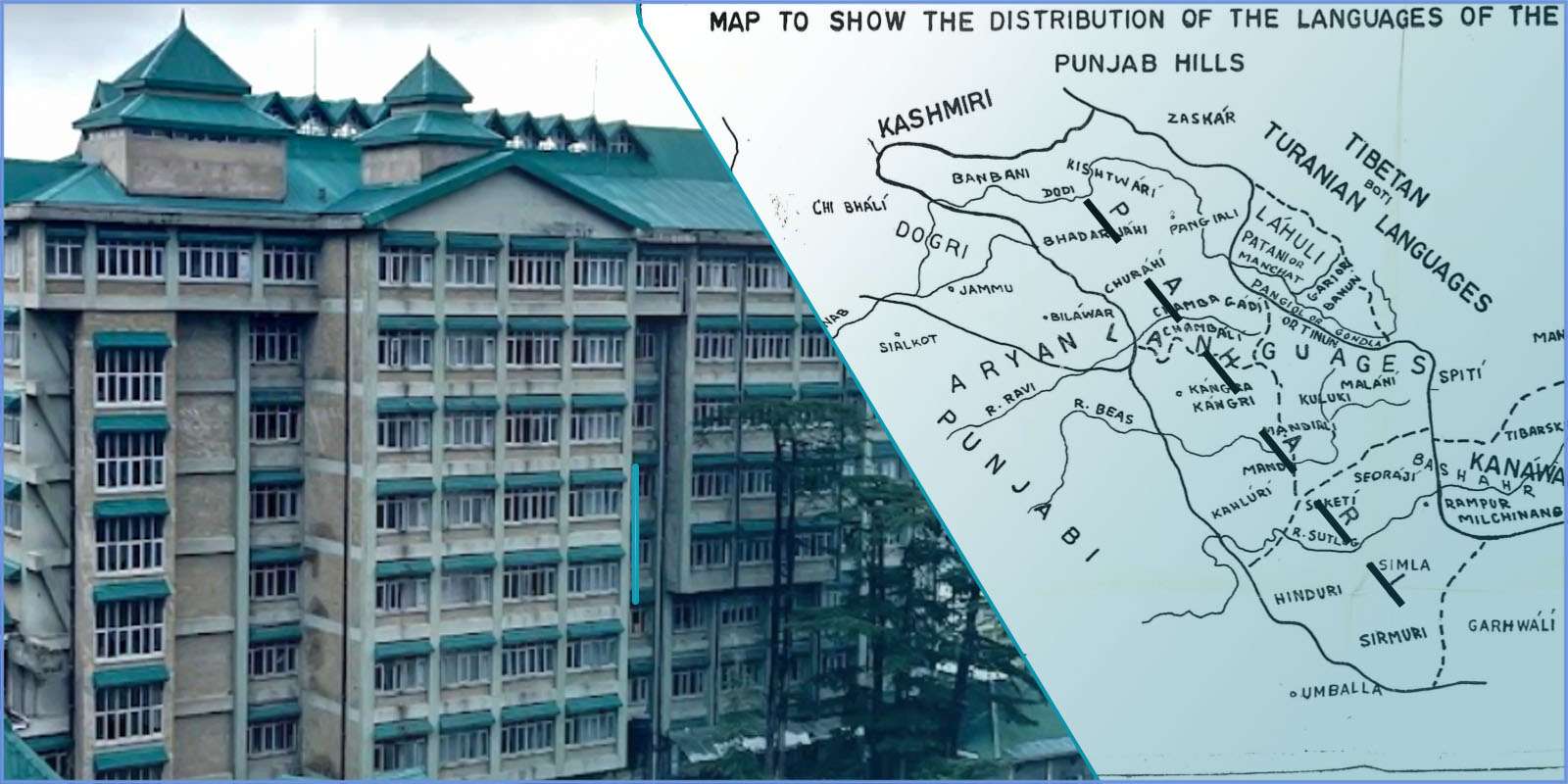

Shimla- November 10, 2021, Himachal Pradesh High Court on Monday passed an order concerning a public interest litigation (PIL) seeking to recognize Pahari (Himachali) as an official language of the state. The petition also sought effective steps on the part of the government to preserve and promote the Pahari language in the State as its culture and language give it a distinct identity.
The Public Interest Litigation was filed by Arsh Dhanotia with a prayer that the state be directed to declare Pahari (Himachali) as one of the official languages in the State of Himachal Pradesh in any script and also promote further research towards a long-term formal Pahari (Himachali) nuclear language structure and nuclear Tankri script.
Bhawani Pratap Singh Kutlahria, the advocate for the petitioner, argued in the court that the State Government be directed to promote Pahari (Himachali) and other local languages as the medium of instruction in primary and middle-level schools as per the New Education Policy, 2020. On behalf of the petitioner, he also prayed the court to direct the state government to include Pahari (Himachali) language as a separate category for the 2021 Census and simultaneously undertake an awareness campaign to create awareness amongst the masses, especially the youth of the State who speak Pahari (Himachali), to get it marked as their mother tongue in the upcoming Census.
A bench of Chief Justice Mohammad Rafiq and Justice Sabina while disposing off the PIL stated,
“The direction as has been prayed for, cannot be issued to the State Government until and unless it is established on record that the Pahari (Himachali) language has its own script and that a common Pahari dialect is spoken throughout the State of Himachal Pradesh. We, however, set the petitioner at liberty to approach the Department of Language Art & Culture to the Government of Himachal Pradesh with his demand for undertaking research to promote a common Pahari (Himachali) nuclear language structure and nuclear Tankri script. If the petitioner approaches the respondents-State through its Additional Chief Secretary (Language Art & Culture) to the Government of Himachal Pradesh) for the prayer made in the Civil Writ Public Interest Litigation, it would be for the said authority to consider the same in accordance with the law.”
Additionally, the petition had emphasised that Sanskrit, which is the second official language of the state, had only 936 speakers according to the 2011 census and Pahari (Himachali) dialect chain which is spoken by more than 40 lakh people was being neglected and has not been made an official language even after having so many speakers.
The petition also highlighted works of Former Chief Minister Late YS Parmar and Former Education Minister Late Narain Chand Parashar towards the promotion of the Pahari (Himachali) language.
What’s Pahari (Himachali) Language, How Many Districts It Covers
It is to be noted that according to the petitioner, Pahari (Himachali) is a combined term used for the Western Pahari dialect chain spoken in Himachal Pradesh and majorly includes Kangri, Mandeali, Chambeali, Kulvi, Mahasu Pahari and Sirmauri. According to him ever since the creation of Himachal Pradesh, there has been a demand for recognition of Pahari (Himachali) under the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and it is also officially listed with 37 more languages as a language which is in significant demand to be included in the scheduled languages category.
In his plea, he also stated that the Himachal Pradesh Vidhan Sabha in 1970 and 2010 have also passed resolutions concerning the promotion and development of Pahari (Himachali).
Environment
Himachal’s Snow Covered Area Has Decreased, Poses Big Threat to State Economy’s Lifelines: Report
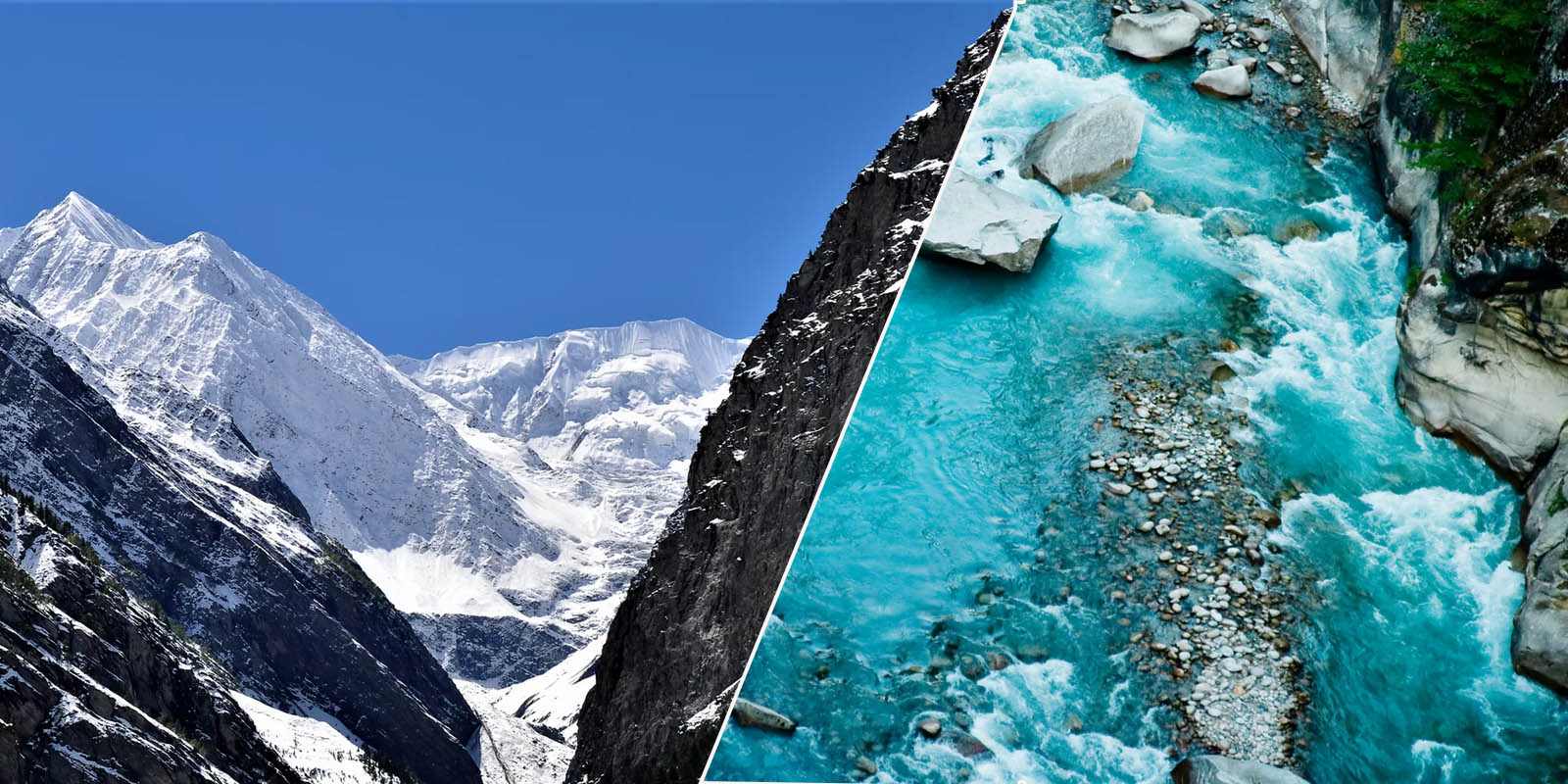

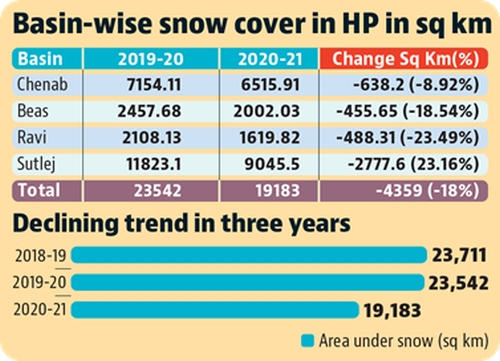
Shimla-The area under snow cover in Himachal Pradesh has declined by 18.5% according to a recent report published by State Centre on Climate Change (SCCC) and Space Application Center (ISRO) Ahmedabad. The report revealed this decreasing trend for the five major river basins in the State.
As the report points out, the high altitude regions of Himachal Pradesh receive precipitation mainly in the form of snow during the winter season. One-third of the geographical area of the state is covered by a thick blanket of snow during the winter season. Rivers like Chenab, Beas, Parvati, Baspa, Spiti, Ravi, Sutlej and its tributaries flowing through Himachal are dependent on snowfall in winter. These rivers mainly feed into the Indus water system and a decline at this rate rings a death knell for water and also food security for millions of people from Himachal to Kashmir, the plains of Punjab, the food bowl of the country.
Using images and data received from satellites, the report states, that the winter precipitation was mapped in all the basins from October 2020 to May 2021 (a period of two years). The findings indicate that there has been an average decrease of 8.92 percent in Chenab basin, 18.54 percent in Beas basin, 23.16 percent in Ravi basin, 23.49 percent in Sutlej basin compared to last year. The ice covered area of Chenab basin was 7154.11 sq km in 2019-20, which has come down to 6515.91 sq km in 2020-21. Similarly, Beas basin was reduced from 2457.68 to 2002.03 square kilometer, Ravi basin from 2108.13 square kilometer to 1619.82 square kilometer and Sutlej from 11823.1 square kilometer to 9045 square kilometers. Overall, the snow covered area was reduced from 23542 square kilometer to 19183 square kilometer in the entire Himachal.
Sutlej Basin covers 45 per cent of the total geographical area of Himachal and it is the longest river of the state. It flows for around 320 kms here, passing through Lahaul and Spiti, Kinnaur, Shimla, Kullu, Mandi, Solan and Bilaspur districts, along its course. The above study shows that the maximum reduction in snow cover has occurred in the Sutlej basin. An area of 4359 square kilometers under snow cover has decreased for the whole state, of which more than half of the Sutlej Basin.
Just two years ago another study had indicated that more than half of glaciers in Sutlej Basin are set to vanish by 2050. Yet another study also showed that the Sutlej basin has the highest 562 number of glacial lakes. These lakes stand the risk of sudden outbursts, which then causes flash floods downstream as the valley has already experienced. So, while the crisis that is unfolding, be it deglaciation, lake formation or reduction in area under snow cover, it seems that the Sutlej river basin is more vulnerable to these changes.
Prakash Bhandari, an environmental researcher and activist and member of Himdhara Collective expressing his concern states that the situation in the Sutlej river basin is certainly indicative of a serious climate emergency and it is critical to look into the drivers of this both local and global.
“The Sutlej basin catchment is the largest and so the changes visible here are more significant. Many factors have worked together to create this crisis which should be studied closely. There is no doubt that global warming is contributing to these changes. But the local conditions also play a role in reducing or increasing its impact”, he says.
The upper reaches of the Sutlej Valley, especially areas like Kinnaur are geologically fragile, with sharp gradients and loose soil strata. Vegetation is in a very small area so the proneness to erosion. We have seen the catastrophic impacts of flashfloods and landslides over the last decade and a half, where crores worth of property has been damaged. This year saw a spate of landslides where lives were lost. “In such a sensitive and also strategically important area, changes in the landscape will have far reaching and irreversible impacts. More construction activities will lead to more deforestation, more erosion”.
Construction of dams has been rampant in the Sutlej valley, a phenomena that started post independence and continues today. If all of the planned dams are built the Sutlej will be cho-a-cloc with more then 150, large and small projects. At the bottom of the valley in Bilaspur is the Bhakra Dam, built almost 6 decades ago, which has a size of 168 sq km and a storage capacity of 9.340 cubic km. Is. This is followed by the Kol Dam which extends for 42 km up to Sunni, which has a total storage capacity of 90 million cubic metres. Nathpa Jhakri Project which is 27.394 kms. is long. When a dam is built, a huge amount of water is stored. The debris of many villages, trees etc. also gets absorbed inside the dam. When water is stagnant, it receives heat from the Sun to form mist in the surrounding area by evaporation and simultaneously generates methane gas. The experience of the lake formed by the Kol dam at Tattapani in Mandi district shows that the area is experiencing heavy haze which was not there earlier.
“In the 30s and 40s, Shikari Devi and Kamrunag used to have snow on the peaks for about 6 months, which now could barely stop for only 2 months. The air route distance of Shikari Devi and Kamrunag is only 26 to 30 kms from Tattapani lake. At the same time, their distance is not much from the cement factories of Darlaghat, Sundernagar”, the elders in the area say. “Today, fog is prevalent and this has also made the area warmer”.
Due to the warming of the weather due to the clouds formed from the mist, the snow has started melting quickly. Apart from this the local crop patterns are affected. Post the 1990s, the Sutlej became a site for run of the river hydroelectric projects using extensive underground tunneling. This involves massive use of explosives for blasting through the mountains. Of the 23,000 MW worth of projects to be constructed in Himachal more than 10,000, a third are from this valley alone. Kinnaur continues to be a hydel powerhouse with 10 run of the river projects in progress and 30 more to be set up including two mega projects of 1500 MW and 1000 MW each. This paints a scary picture.
Interactive Sutlej River-Basin Map indicate Hydropower Station location
It is not just the hydro-electric dams but unplanned tourism and other development activities like mining, cement plants, road expansion and mindless construction across the high Himalayan regions have also add to the shift in local weather patterns, land use changes and thus the ecological crisis. But the reason why we should put the limelight on hydropower is that this is being pushed as “Green Energy”, in the name of climate change mitigation. As opposed to other forms of generating power, hydropower projects are said to cause lesser carbon emissions, which is why there has been a global push to shift to renewable resources. But the climate emergency in the Himalayas has put a question mark on ‘water’ as a renewable resource.
The question then arises that with all this data indicating a steady decline in river discharge and snow cover have our planners and policy makers not considered what will happen to these projects? Will they be able to generate the power they propose to? The people of Himalaya have to wake up to this wastage of public resources. Scarce funds should be diverted to better planning for securing local livelihoods by protecting the forest ecosystems and water sources for the future.
Author: Gagandeep Singh-From Himdhara (Environment Research and Action Collective)
Feature Images: unsplash/@raimondklavins
HW Community
Himachal: Warnings of Delta Plus Virulence Fall on Deaf Ears, No Restriction on Visitors from Affected States

Shimla-Yesterday, the Centre government directed the state governments to take immediate measure in wake of the spread of more infectious Delta Plus variant. As the Delta Plus variant is posing a threat of the third wave, the states were told to take steps like preventing crowds, increase testing, more focus on surveillance, contact tracing and put boosting vaccine coverage on a priority basis. Following it, Himachal Pradesh Government might have announced an alert over Delta plus variant, but there wasn’t any follow up on instructions passed by scientists and health experts to take strict restrictive measures ahead of the impending third wave.
To make it worse, high rank officials and political leaders were seen flouting Covid-19 SOPs on several occasion, which sent wrong messages to the masses. The pictures and videos showing flouting of Covid appropriate behavior by Chief Minister Jairam Thakur and Directorial General of Police, Sanjay Kundu, alongwith other staff for Anupam Kher is the most recent to mention. A group photograph and video of the same were widely circulated on social media and invited huge criticism from the people.
So far, the state has not reported any case of the Delta Plus variant. But the neighboring states – Punjab, Haryana, and Jammu & Kashmir – reported their first cases yesterday. This puts the boarding areas, like in Una district, at a higher risk. Chief Secretary to HP Government, Anil Khachi, yesterday said samples have been sent for genome sequencing.
Despite repeated warnings of Delta plus variant (B.1.617.2.1.), Himachal Pradesh has thrown its borders open to all and lifted all restrictions for inter-state travel in just one go. From June 23 onwards, the state government removed the condition for registering on the e-pass portal for visitors intending to enter the state. In the Cabinet meeting held on June 22, 201, the government first decided that e-pass restrictions would be removed from July 1, but later it changed the decision and instead implemented it immediately.
This haphazard decision is said to have come under huge pressure from the hospitality industry – the worst-hit sector, leading to financial crisis and mass unemployment among its stakeholders. Related associations had been approaching Chief Minister Jairam Thakur with their pleas to provide relief, but mostly faced disappointment. The stakeholders say the state government didn’t provide any significant relief, which is making the survival of the industry difficult.
Also Read: Read Eight Reliefs That Himachal’s Devastated Tourism Industry Seeks from HP Govt
Also, stakeholder of the industry, especially hoteliers, had been demanding the removal of restrictions and conditions on the entry of tourists to Himachal so that they could fetch the remaining peak tourist season.
With its inability to offer relief, the HP Government took the chance to waive off restrictions in a haste.
At the same time, the state government has decided to conduct offline examinations for the undergraduate classes starting from July. A section of the students had been condemning the HP government for scheduling exams without vaccinating students. Some student bodies had been asking the government as to why online classes were possible but not online exams.
The state government also waived off restrictions on timings for the opening of markets/shops.
As scientists and health experts warn of the virulence of the new variant and with neighboring states already on alert after reporting cases of the new variant, the HP government hasn’t even mentioned any intention to at least put a check on the visitor from the states where cases of Delta Plus are being reported. Carrying an RT-PCR negative report for visitors from such states/cities would have been a wiser step.
Officially, the state is on alert, but no measures have been announced to check the entry and spread of the variant into the state. The state government does speak of preparing for the anticipated third wave, but there is hardly any long-term preventive strategy. The Covid appropriate behavior is hard to adopt when markets and tourist places are crowded with visitors.
Why Delta Plus is a Big Concern
The World Health Organization (WHO) has labelled the Delta variant as ‘Variant of Concern’.
The Centre and scientific/medical institutes in India also agree with that Delta Plus as a variant of concern and could be the cause of impending third wave. Last Tuesday, based on the findings of INSACOG, the Union Health Ministry had alerted and advised Maharashtra, Kerala and Madhya Pradesh regarding the Delta Plus variant of COVID19.
INSACOG had warned that the Delta Plus variant has increased transmissibility, stronger binding to receptors of lung cells, potential reduction in monoclonal antibody response.
“Delta variant is more resistant to medication, treatment and vaccination. Therefore, people who have been vaccinated can still be affected by this variant and can go on to get a clinical illness, Archana Dhawan Bajaj, director, Nurture IVF, told a national English Daily.
“Neutralising antibodies against this variant post-vaccination seem to be nearly five times lower in people who have already been vaccinated than the other variants,” she said.
Further, Dr Raman Gangakhedkar, ex-Head Scientist of Epidemiology and communicable diseases, ICMR, has also expressed concern over the reports that Delta Plus has reported pathophysiologic change and affecting different organs. Dr Raman says that it could transfer from cell to cell and would more likely produce neurological symptoms as a common manifestation.
So far India has reported 51 cases of the Delta Plus variant.
Delta Plus variant is a variant of Delta with an additional mutation -B.1.617.2.1.











 Home Decor Ideas 2020
Home Decor Ideas 2020
