Environment
SC’s Forest Diversion Regulation a Blockade on Forest Rights Act Implementation in Himachal: Himdhara

Shimla–Himdhara Collective, a Himachal-based environment research and action group, has released a report on the implications of the regulation imposed by the Supreme Court on forest diversion under the Forest Rights Act 2006 in Himachal, through a series of orders passed last year. This brought to a screeching halt the implementation of Section 3(2) of the FRA which grants powers to gram sabhas and Divisional Forest Officers to divert upto 1 hectare of forest land for 13 types of village welfare activities like roads, schools, community centres, PDS shops etc.
The court orders were based on the conclusions drawn by a Supreme Court Monitoring Committee, headed by a retired PCCF, V.P Mohan, that the diversions were leading to green felling and deforestation in the state. Initially, a stay was imposed on all green felling in the state (in a matter of forest diversions under FCA 1980 and FRA 2006) on 11th March 2019. This stay was partially relaxed but the Supreme court sought all FRA proposals to be brought before it for further diversion.
The report titled ‘Missing the forest for Trees’, assesses the ground reality behind the conclusions drawn by the Supreme Court Monitoring Committee based on which these diversions have been restricted.
“We have found that the Supreme court’s orders need to be reviewed because the alarm raised by the V.P Mohan committee with regard to FRA was a false one”,
stated authors of the report which is based on analysis of RTI information as well as field research.
RTI data sought from the Forest department for all cases under section 3(2) of the Forest Rights Act 2006 from 2014 to 2019 (up to January 2019), was analysed to reveal that 17237 trees were felled in an area of 887.56 hectares for 1959 activities in 41 of the 45 forest divisions of the state.
Roads, followed by schools and community centres dominate the type of activities carried out. Of the total land diverted 91% is for roads. It was found that almost 64% of these diversions showed ‘nil’ trees felled. The average number of trees felled per hectare is very low (19.52) and it may be induced that most activities have been carried out in areas with open forest or no trees.
Rohru (Shimla), Nachan(Mandi), Kinnaur and Chopal were some of the divisions which had a large number of diversions, again mostly for roads.
Case studies we carried out in Mandi and Kangra district showed the desperate need for amenities like village link roads and schools. In Himachal, there remain about 41% villages that have no road connectivity which affects access to health, education and market centres.
On the other hand, large development activities like four lane highways, hydropower projects and transmission lines, have had a much larger ecological footprint in terms of tree loss in the state compared to the very minute, incomparable diversions under FRA.
The report also finds that as far as green cover is concerned in the period corresponding to the high number of forest diversions under FRA (2015-2019), the forest survey of India’s statistics show a 333 sq.km increase in the forest cover.
Why development rights under FRA important for Himachal?
1.No Land available with revenue departments and panchayats for ‘welfare activities’ thus forest land only option
The report concludes that given the fact that 2/3rd of the geographical area of the state is recorded ‘forest area’ where strict forest laws have restricted non-forest use, the FRA provides relief for communities to access basic welfare facilities, which should be seen as their fundamental right and therefore should not be hindered.
2.Cumbersome, costly and lengthy process under FCA 1980
Before FRA it was the Forest Conservation Act, 1980 which governed forest diversion even for small local development activities. This required not only permission from the Central Government (MoEFCC Regional or Delhi Office) but also warranted that user agencies deposit funds (Net Present Value of trees) to carry out Compensatory Afforestation. The whole diversion process under FCA was cumbersome, lengthy and costly, and thus a major hurdle in providing the rural areas, especially remote areas, access to basic welfare development facilities.
“The section 3(2) of the FRA provides relief for both governmental departments and local communities as it overrides the FCA and puts in place a simple and decentralized process for diversion”states the report.
3.FRA is meant to correct the problems that were posed by strict central forest laws
The Forest Rights Act was passed by the parliament of India in 2006 recognising that across the country there are lakhs of communities dependent on land which is legally categorised as ‘forest land’ and are unable to exercise their basic livelihood and development rights due to extremely strict forest laws. Under this act’s Section 3(1), forest-dependent communities can file claims for their individual and community rights exercised before the cut-off date of 13th December 2005.
“As it is Himachal has been sluggish with FRA implementation and only 136 titles have been issued under section 3(1). But atleast the government was proactive with the implementation of section 3(2). With the Supreme court orders regulating this provision, there seems to be an impression amongst the implementing agencies and officials that there is an over-all blockade on FRA in the state”
added members of the collective.
The report has recommended that the state government and nodal agency for the Act – the Central Ministry of Tribal Affairs, put forth the case in favour of section 3(2) of the FRA strongly in front of the Supreme Court and also move swiftly to ensure implementation of all provisions of this law in Himachal.
Environment
Dharamshala’s first Solar Power Project Inaugurated, 750-kilowatt project to generate 20,000 units a day
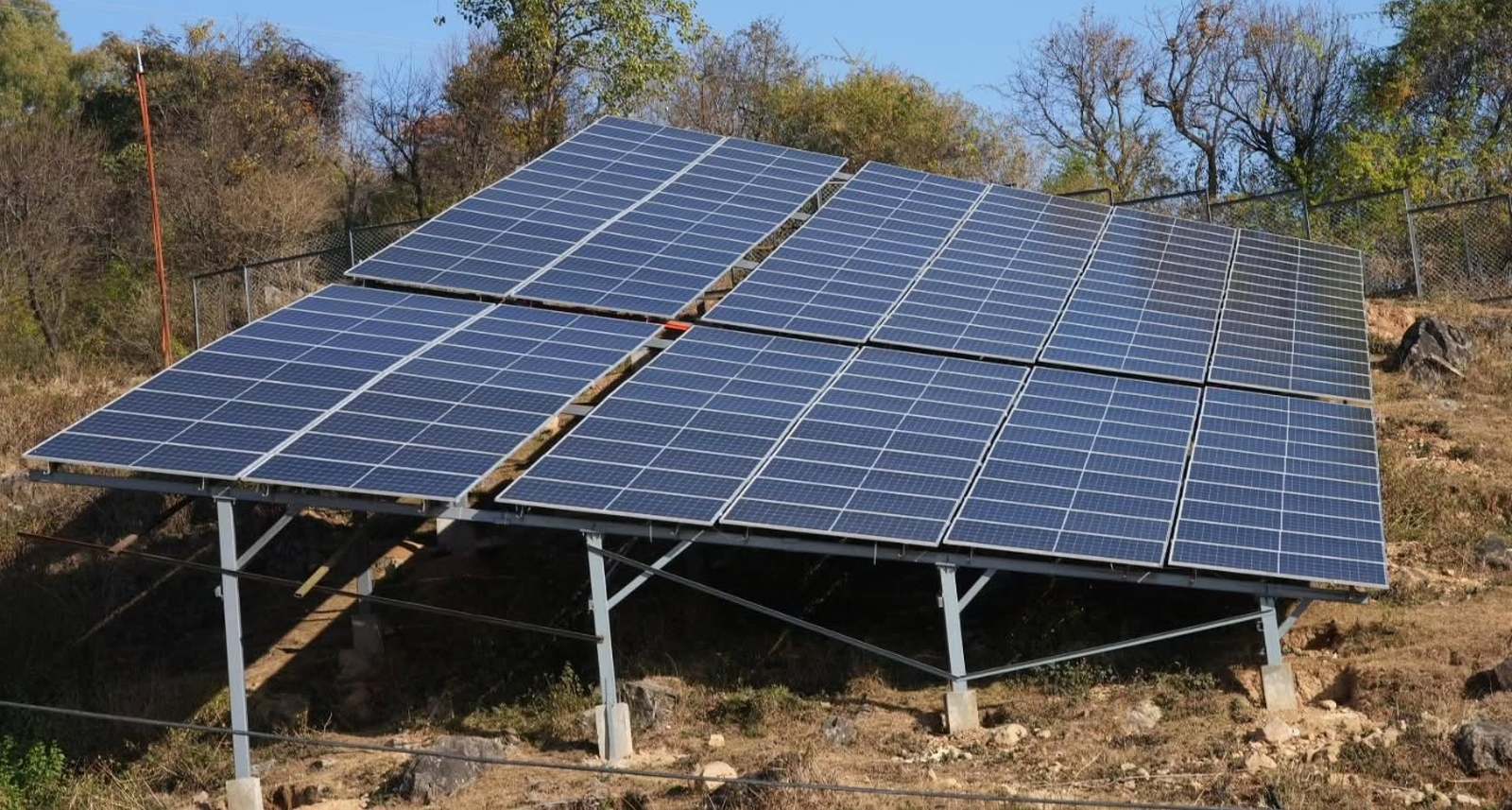

Kangra-Dharamshala’s first 750-kilowatt solar power project, built for Rs. 4.74 crore, was inaugurated on Friday. Spanning 8,500 square meters of land, this project will generate approximately 2,000 units of electricity daily, yielding a monthly income of Rs. 2.80 lakh.
Starting in October 2023, the project’s construction work was completed in November 2024.
According to the government, the Himachal Pradesh State Electricity Board Limited (HPSEBL) has signed an agreement to purchase electricity generated from this project. The government claimed that the project features 1,364 solar panels equipped with comprehensive safety measures, including lightning and fire protection, and an earthing and bonding system to ensure electrical safety.
The government said seven solar power projects with a combined capacity of 72 megawatts would soon be allocated. Surveys and studies are underway for eight projects with a total capacity of 325 megawatts. For the first time, the government was moving towards developing 200 panchayats as “Green Panchayats” by installing 200-kilowatt ground-mounted solar plants, the government claimed.
As per the government, the 32-megawatt Pekhubela solar energy project in the Una district was dedicated to the public on April 15, 2024. From April to October 2024, the project generated 34.19 million units of electricity in six and a half months, earning Rs. 10.16 crore. Additionally, the 5-megawatt solar energy project in Bhanjal (Una) was commissioned on November 30, 2024, while the construction of the 10-megawatt Aghlaur solar energy project is expected to be completed shortly.
The government said it aims to make Himachal Pradesh India’s first ‘Green Energy State’ by 2026.
Environment
Himachal’s Snow Covered Area Has Decreased, Poses Big Threat to State Economy’s Lifelines: Report

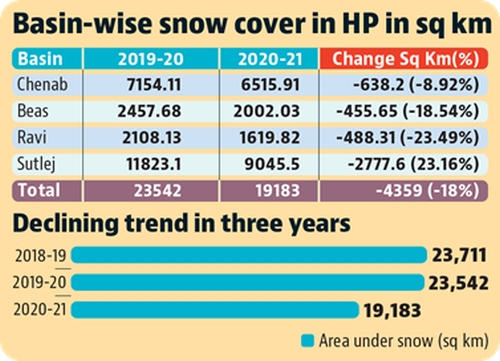
Shimla-The area under snow cover in Himachal Pradesh has declined by 18.5% according to a recent report published by State Centre on Climate Change (SCCC) and Space Application Center (ISRO) Ahmedabad. The report revealed this decreasing trend for the five major river basins in the State.
As the report points out, the high altitude regions of Himachal Pradesh receive precipitation mainly in the form of snow during the winter season. One-third of the geographical area of the state is covered by a thick blanket of snow during the winter season. Rivers like Chenab, Beas, Parvati, Baspa, Spiti, Ravi, Sutlej and its tributaries flowing through Himachal are dependent on snowfall in winter. These rivers mainly feed into the Indus water system and a decline at this rate rings a death knell for water and also food security for millions of people from Himachal to Kashmir, the plains of Punjab, the food bowl of the country.
Using images and data received from satellites, the report states, that the winter precipitation was mapped in all the basins from October 2020 to May 2021 (a period of two years). The findings indicate that there has been an average decrease of 8.92 percent in Chenab basin, 18.54 percent in Beas basin, 23.16 percent in Ravi basin, 23.49 percent in Sutlej basin compared to last year. The ice covered area of Chenab basin was 7154.11 sq km in 2019-20, which has come down to 6515.91 sq km in 2020-21. Similarly, Beas basin was reduced from 2457.68 to 2002.03 square kilometer, Ravi basin from 2108.13 square kilometer to 1619.82 square kilometer and Sutlej from 11823.1 square kilometer to 9045 square kilometers. Overall, the snow covered area was reduced from 23542 square kilometer to 19183 square kilometer in the entire Himachal.
Sutlej Basin covers 45 per cent of the total geographical area of Himachal and it is the longest river of the state. It flows for around 320 kms here, passing through Lahaul and Spiti, Kinnaur, Shimla, Kullu, Mandi, Solan and Bilaspur districts, along its course. The above study shows that the maximum reduction in snow cover has occurred in the Sutlej basin. An area of 4359 square kilometers under snow cover has decreased for the whole state, of which more than half of the Sutlej Basin.
Just two years ago another study had indicated that more than half of glaciers in Sutlej Basin are set to vanish by 2050. Yet another study also showed that the Sutlej basin has the highest 562 number of glacial lakes. These lakes stand the risk of sudden outbursts, which then causes flash floods downstream as the valley has already experienced. So, while the crisis that is unfolding, be it deglaciation, lake formation or reduction in area under snow cover, it seems that the Sutlej river basin is more vulnerable to these changes.
Prakash Bhandari, an environmental researcher and activist and member of Himdhara Collective expressing his concern states that the situation in the Sutlej river basin is certainly indicative of a serious climate emergency and it is critical to look into the drivers of this both local and global.
“The Sutlej basin catchment is the largest and so the changes visible here are more significant. Many factors have worked together to create this crisis which should be studied closely. There is no doubt that global warming is contributing to these changes. But the local conditions also play a role in reducing or increasing its impact”, he says.
The upper reaches of the Sutlej Valley, especially areas like Kinnaur are geologically fragile, with sharp gradients and loose soil strata. Vegetation is in a very small area so the proneness to erosion. We have seen the catastrophic impacts of flashfloods and landslides over the last decade and a half, where crores worth of property has been damaged. This year saw a spate of landslides where lives were lost. “In such a sensitive and also strategically important area, changes in the landscape will have far reaching and irreversible impacts. More construction activities will lead to more deforestation, more erosion”.
Construction of dams has been rampant in the Sutlej valley, a phenomena that started post independence and continues today. If all of the planned dams are built the Sutlej will be cho-a-cloc with more then 150, large and small projects. At the bottom of the valley in Bilaspur is the Bhakra Dam, built almost 6 decades ago, which has a size of 168 sq km and a storage capacity of 9.340 cubic km. Is. This is followed by the Kol Dam which extends for 42 km up to Sunni, which has a total storage capacity of 90 million cubic metres. Nathpa Jhakri Project which is 27.394 kms. is long. When a dam is built, a huge amount of water is stored. The debris of many villages, trees etc. also gets absorbed inside the dam. When water is stagnant, it receives heat from the Sun to form mist in the surrounding area by evaporation and simultaneously generates methane gas. The experience of the lake formed by the Kol dam at Tattapani in Mandi district shows that the area is experiencing heavy haze which was not there earlier.
“In the 30s and 40s, Shikari Devi and Kamrunag used to have snow on the peaks for about 6 months, which now could barely stop for only 2 months. The air route distance of Shikari Devi and Kamrunag is only 26 to 30 kms from Tattapani lake. At the same time, their distance is not much from the cement factories of Darlaghat, Sundernagar”, the elders in the area say. “Today, fog is prevalent and this has also made the area warmer”.
Due to the warming of the weather due to the clouds formed from the mist, the snow has started melting quickly. Apart from this the local crop patterns are affected. Post the 1990s, the Sutlej became a site for run of the river hydroelectric projects using extensive underground tunneling. This involves massive use of explosives for blasting through the mountains. Of the 23,000 MW worth of projects to be constructed in Himachal more than 10,000, a third are from this valley alone. Kinnaur continues to be a hydel powerhouse with 10 run of the river projects in progress and 30 more to be set up including two mega projects of 1500 MW and 1000 MW each. This paints a scary picture.
Interactive Sutlej River-Basin Map indicate Hydropower Station location
It is not just the hydro-electric dams but unplanned tourism and other development activities like mining, cement plants, road expansion and mindless construction across the high Himalayan regions have also add to the shift in local weather patterns, land use changes and thus the ecological crisis. But the reason why we should put the limelight on hydropower is that this is being pushed as “Green Energy”, in the name of climate change mitigation. As opposed to other forms of generating power, hydropower projects are said to cause lesser carbon emissions, which is why there has been a global push to shift to renewable resources. But the climate emergency in the Himalayas has put a question mark on ‘water’ as a renewable resource.
The question then arises that with all this data indicating a steady decline in river discharge and snow cover have our planners and policy makers not considered what will happen to these projects? Will they be able to generate the power they propose to? The people of Himalaya have to wake up to this wastage of public resources. Scarce funds should be diverted to better planning for securing local livelihoods by protecting the forest ecosystems and water sources for the future.
Author: Gagandeep Singh-From Himdhara (Environment Research and Action Collective)
Feature Images: unsplash/@raimondklavins
Environment
Chemical Waste Allegedly Poisons Ground Water in Solan Village, Killing Cattle and Causing Diseases in Villagers

Solan- The Shivalik Solid Waste Management Plant was set up at Village, Majra, Nalagarh, in District Solan 15 years ago. A no-objection certificate (NOC) was obtained from the Panchayat by telling it that it was an environment project. But, later, the villagers found that they were misled for obtaining this NOC. Only when this Plant was built, the villagers came to know that hazardous chemical solid toxic waste of the different factories of Himachal Pradesh was to be brought to this Solid Waste plant and that it was responsible for treating this solid waste.
When the cattle allegedly started dying and villagers fell ill due to various diseases, the villagers came to know that the Plant had contaminated the groundwater by dumping the waste into the ground instead of treating it.
A villager, Joginder Singh, Village Majra, alleged that villagers made many complaints to Pollution Control Board, as well as, various other higher authorities but till date, no action was been taken against the company.
He alleged that due to this poisonous water, their cattle have died and even the villagers have fallen victim to many serious diseases.
Eventually, Singh wrote a letter to the Chief Justice of the Himachal Pradesh High Court, in which it alleged that for the last 15 years, the aforesaid Plant was dumping the solid waste in the ground by covering it with soil, without proper treatment. Over time, the water of natural sources, wells and bore-wells of Panchayat Mazra and the surrounding villages became poisonous due to seepage of chemically contaminated water of this Plant into the ground and resultantly foul smell is emanating from the water.
He urged the Court to pass necessary directions for taking stringent action against the Shivalik solid Waste Management and save the villagers from the hazardous effect of this contaminated water.
A Division Bench comprising Acting Chief Justice Ravi Malimath and Justice Jyotsna Rewal Dua took suo moto cognizance of this letter, making it a Public Interest Litigation.
While hearing this petition, the HP High Court on September 27, 2021, issued a notice to the Chief Secretary, Member Secretary, H.P. State Environment Protection and Pollution Control Board, and the Deputy Commissioner, Solan, in a matter pertaining to the contamination of the water of Wells and Bore-Wells of the surrounding areas due to Chemical Waste of Shivalik Solid Waste Management Plant set.
The court posted the matter after two weeks and also directed the respondents to file their replies by the next date.













 Home Decor Ideas 2020
Home Decor Ideas 2020
