Environment
Himachal at high risk of floods due rise in number of Supra glacial lakes formed by melting snow: Study
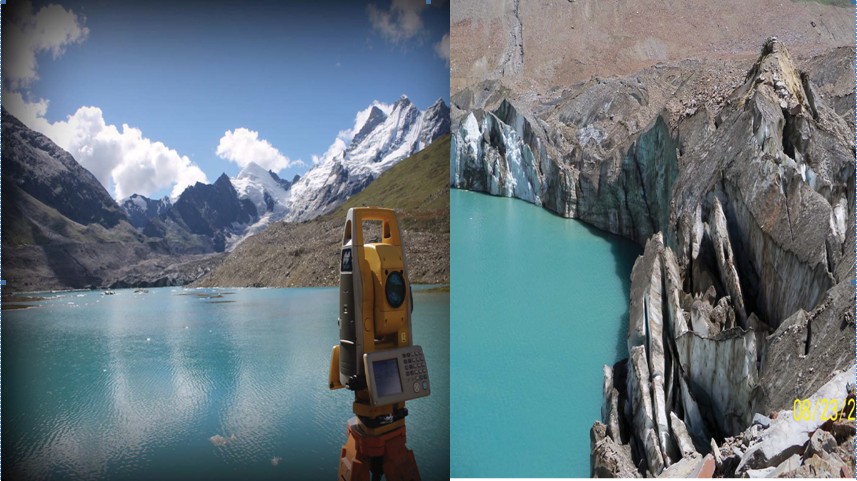

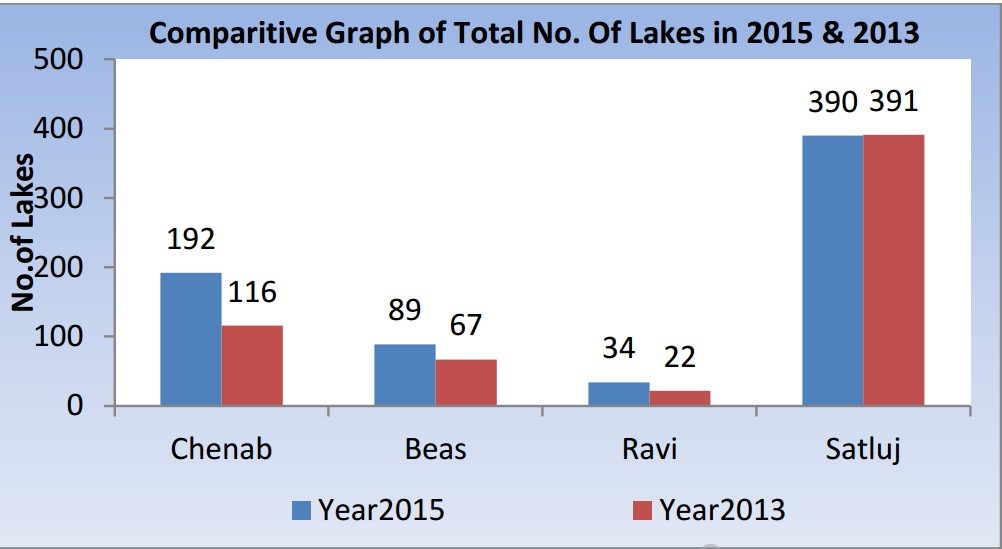
According to the studies carried out by the Centre, number of such lakes in Satluj basin has increased from 38 in 1993-94 to 390 in 2015.
SHIMLA- Scientists have already warned Himachal Pradesh about quakes and, indeed, abnormal seismic activity in the Himalayan belt was observed during past couple of years. Now, the State Centre on Climate Change of the State Council for Science Technology & Environment has warned Himachal Pradesh regarding devastating floods as melting of glaciers is causing formation of more lakes. Outburst of these lakes could unleash massive amount of water leading to floods.
The government has been advised to regularly monitor changes in these lakes, especially the smaller one in the higher Himalayan region of the State. Attention of government in this case is critical for averting any future eventuality in Himachal and loss of precious human lives, said the Centre.
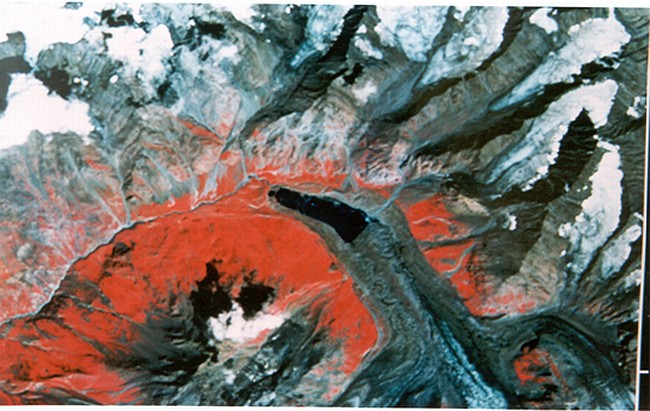

Example: Photographical representation of how the Moraine Dammed Glacial Lake looks like in the Satellite Image-vis-à-vis the Field
To understand the situation, which is in this case is rapid growth in formation of small lakes due to retrieval of glaciers, let’s go through some review.
The state of Himachal Pradesh invariably experiences flash floods, the cause of which is unknown. In the year 2000, the Satluj valley experienced the heaviest floods causing economic loss of more than 800 crores. The cause of this flood event was not known to the experts that whether the floods were caused by cloud bursting or due to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOF) phenomena as it started from the Tibetan Himalayan Region.

Satellite and Field photograph of Moraine Dammed lake at the Snout of the Geepang Gath Glacier in Chandra Basin,District Lahaul & Spiti, H.P.
The formation of landslide dammed lakes in high altitude zones such as Parachoo in the upper catchment of Spiti basin in Tibet caused tremendous threat to the life and property located in the downstream areas since its inception in the year 2004.
The recent tragedy of 2013 in the Uttrakhand Himalaya has also been correlated with the bursting of a lake having a total area of about 08 hectare in front of the snout of the Chorabari glaciers that caused widespread damage in the downstream areas besides the heavy rainfall in the area.
Causes and Threats of GLOF
As per various studies carried out in the past, Himalayan glaciers are in a state of general retreat since 1850. In the Himalayas, during the retreating phase a large number of lakes are being formed either at the snout of the glacier as a result of damming of the morainic material known as moraine dammed lakes or supra glacial lakes formed in the glacier surface area.
Most of these lakes are formed by the accumulation of vast amounts of water from the melting of snow and by blockade of end moraines located in the down valleys close to the glaciers. In addition, the lakes can also be formed due to landslides causing artificial blocks in the waterways. The sudden break of a moraine/block may generate the discharge of large volumes of water and debris from these glacial lakes and water bodies causing flash floods namely GLOF.
The sudden bursts of lakes can happen due to erosion, a buildup of water pressure, an avalanche of rock or heavy snow, an earthquake, or if a large enough portion of a glacier breaks off and massively displaces the waters in a glacial lake at its base. There are number of such events that have happened in Nepal Himalayas but no such event has been reported so far from Indian Himalayas.
According to the State Centre on Climate Change of the State Council for Science Technology & Environment, which has been carrying different studies in the Himachal Himalaya since 1993, number lakes has increased manifold in last two decades.
Lake Formation Increasing River Basins
Satluj Basin
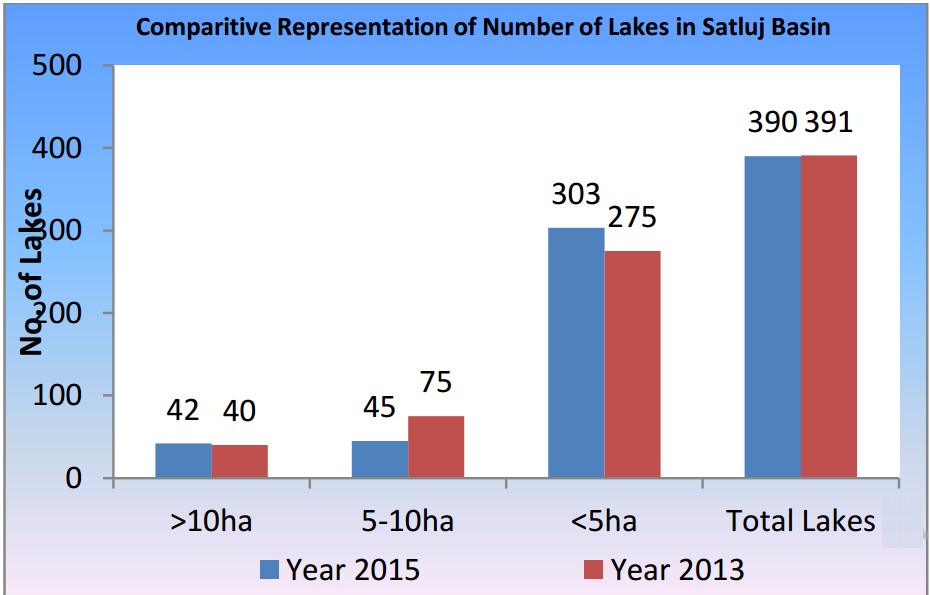
According to the studies carried out by the Centre, number of such lakes in Satluj basin has increased from 38 in 1993-94 to 390 in 2015.
Out of these 390 lakes, 42 lakes have area more than 10 hectare, 45 between 5-10 hectare, and remaining 303 lakes have an area less than 5 hectare.
Chenab Basin
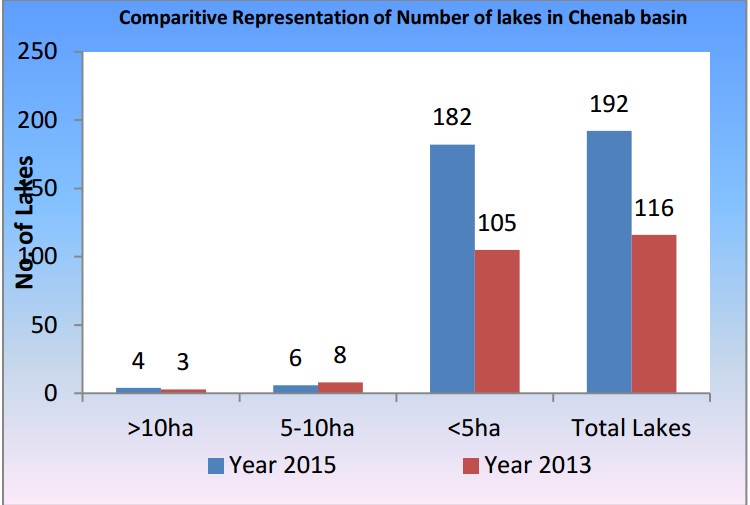
Likewise the Chenab basin which mainly originates from the Himachal Himalaya, total number of lakes has increased from 116 in 2013 to 192 in 2015, which is almost four times than the number of lakes identified during 2001.
Out of these 192 lakes, 04 lakes have area more than 10 hectare, 6 lakes between 5-10 hectare and 182 are the small ones having area less than 5 hectare.
Beas Basin
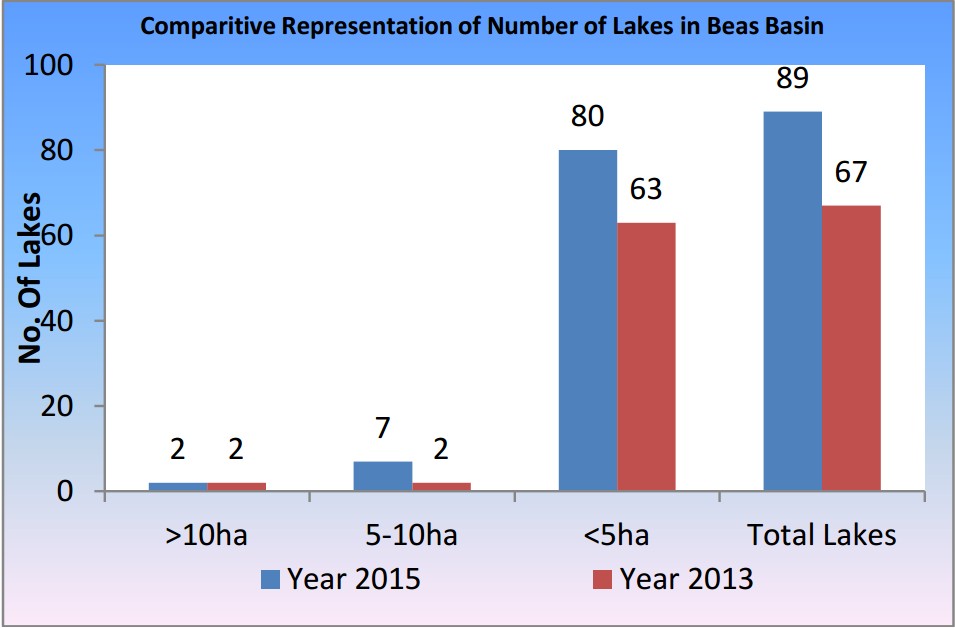
In the Beas basin, number of lakes has gone up from 67 lakes during 2013 to 89 lakes in 2015, revels satellite data. Further analysis of these 89 lakes reveals that 80 lakes are smaller one having area less than 5 hectare, 07 lakes with aerial range between 5-10 hectare and 02 lakes which are having area more than 10 hectare.
Ravi Basin
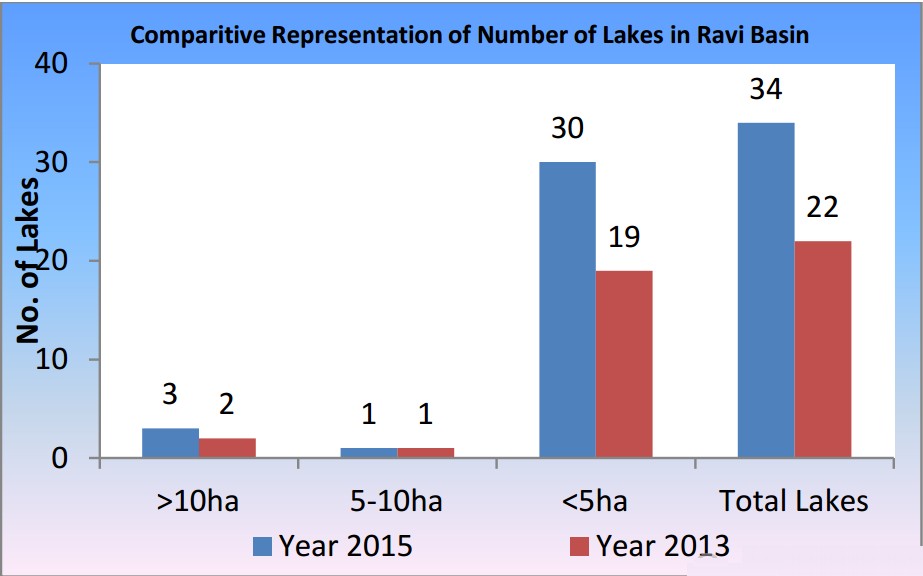
The Ravi basin had total 22 lakes in 2013, which has now increased to 34 in 2015. When seen based on aerial distribution ,it is found that 03 lakes are having area more than 10 hectare, only 01 lake is having area between 5-10 hectare and 30 lakes are such which have area less than 5 hectare.
Need of time
Based on the above analysis carried out by the Centre for the year 2015, it is evident that there is a considerable increase in the number of moraine dammed lakes (GLOFs) in each basin which reflects that formation of such lakes in the Higher Himalayan region is indicating an increasing trend. The higher number of smaller lakes i.e. lakes with area less than 5 hectare indicates that the effect of the climatic variations is more pronounced on the glaciers of the Himalayan region resulting in the formation of small lakes in front of the glacier snouts due to the damming of the morainic material.
The lakes with area more than 10 hectare and those with area between 5-10 hectare are more vulnerable sites for causing damage in case of bursting of any one of them.
Therefore, a proper monitoring and change analysis of all such lakes in higher Himalayan region of the State is critical for averting any future eventuality in Himachal Pradesh, so that the precious human lives are saved.
Another aspect of this report is about climate change caused by rising carbon emissions. Himachal need to pay attention to check air pollution. Currently, the Chief Minister Virbhadra Singh and his minister hardly believe in theory of global warming or glacier melting. Annoyed over NGT’s ban on fossil fuel vehicles into Rohtang Pass region, the CM had claimed that there are actually no glaciers around Rohtang. Vehicular emissions are excess and widespread with literally no check on it.
Environment
Himachal’s Snow Covered Area Has Decreased, Poses Big Threat to State Economy’s Lifelines: Report

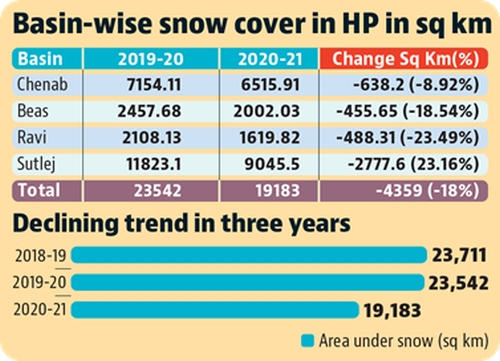
Shimla-The area under snow cover in Himachal Pradesh has declined by 18.5% according to a recent report published by State Centre on Climate Change (SCCC) and Space Application Center (ISRO) Ahmedabad. The report revealed this decreasing trend for the five major river basins in the State.
As the report points out, the high altitude regions of Himachal Pradesh receive precipitation mainly in the form of snow during the winter season. One-third of the geographical area of the state is covered by a thick blanket of snow during the winter season. Rivers like Chenab, Beas, Parvati, Baspa, Spiti, Ravi, Sutlej and its tributaries flowing through Himachal are dependent on snowfall in winter. These rivers mainly feed into the Indus water system and a decline at this rate rings a death knell for water and also food security for millions of people from Himachal to Kashmir, the plains of Punjab, the food bowl of the country.
Using images and data received from satellites, the report states, that the winter precipitation was mapped in all the basins from October 2020 to May 2021 (a period of two years). The findings indicate that there has been an average decrease of 8.92 percent in Chenab basin, 18.54 percent in Beas basin, 23.16 percent in Ravi basin, 23.49 percent in Sutlej basin compared to last year. The ice covered area of Chenab basin was 7154.11 sq km in 2019-20, which has come down to 6515.91 sq km in 2020-21. Similarly, Beas basin was reduced from 2457.68 to 2002.03 square kilometer, Ravi basin from 2108.13 square kilometer to 1619.82 square kilometer and Sutlej from 11823.1 square kilometer to 9045 square kilometers. Overall, the snow covered area was reduced from 23542 square kilometer to 19183 square kilometer in the entire Himachal.
Sutlej Basin covers 45 per cent of the total geographical area of Himachal and it is the longest river of the state. It flows for around 320 kms here, passing through Lahaul and Spiti, Kinnaur, Shimla, Kullu, Mandi, Solan and Bilaspur districts, along its course. The above study shows that the maximum reduction in snow cover has occurred in the Sutlej basin. An area of 4359 square kilometers under snow cover has decreased for the whole state, of which more than half of the Sutlej Basin.
Just two years ago another study had indicated that more than half of glaciers in Sutlej Basin are set to vanish by 2050. Yet another study also showed that the Sutlej basin has the highest 562 number of glacial lakes. These lakes stand the risk of sudden outbursts, which then causes flash floods downstream as the valley has already experienced. So, while the crisis that is unfolding, be it deglaciation, lake formation or reduction in area under snow cover, it seems that the Sutlej river basin is more vulnerable to these changes.
Prakash Bhandari, an environmental researcher and activist and member of Himdhara Collective expressing his concern states that the situation in the Sutlej river basin is certainly indicative of a serious climate emergency and it is critical to look into the drivers of this both local and global.
“The Sutlej basin catchment is the largest and so the changes visible here are more significant. Many factors have worked together to create this crisis which should be studied closely. There is no doubt that global warming is contributing to these changes. But the local conditions also play a role in reducing or increasing its impact”, he says.
The upper reaches of the Sutlej Valley, especially areas like Kinnaur are geologically fragile, with sharp gradients and loose soil strata. Vegetation is in a very small area so the proneness to erosion. We have seen the catastrophic impacts of flashfloods and landslides over the last decade and a half, where crores worth of property has been damaged. This year saw a spate of landslides where lives were lost. “In such a sensitive and also strategically important area, changes in the landscape will have far reaching and irreversible impacts. More construction activities will lead to more deforestation, more erosion”.
Construction of dams has been rampant in the Sutlej valley, a phenomena that started post independence and continues today. If all of the planned dams are built the Sutlej will be cho-a-cloc with more then 150, large and small projects. At the bottom of the valley in Bilaspur is the Bhakra Dam, built almost 6 decades ago, which has a size of 168 sq km and a storage capacity of 9.340 cubic km. Is. This is followed by the Kol Dam which extends for 42 km up to Sunni, which has a total storage capacity of 90 million cubic metres. Nathpa Jhakri Project which is 27.394 kms. is long. When a dam is built, a huge amount of water is stored. The debris of many villages, trees etc. also gets absorbed inside the dam. When water is stagnant, it receives heat from the Sun to form mist in the surrounding area by evaporation and simultaneously generates methane gas. The experience of the lake formed by the Kol dam at Tattapani in Mandi district shows that the area is experiencing heavy haze which was not there earlier.
“In the 30s and 40s, Shikari Devi and Kamrunag used to have snow on the peaks for about 6 months, which now could barely stop for only 2 months. The air route distance of Shikari Devi and Kamrunag is only 26 to 30 kms from Tattapani lake. At the same time, their distance is not much from the cement factories of Darlaghat, Sundernagar”, the elders in the area say. “Today, fog is prevalent and this has also made the area warmer”.
Due to the warming of the weather due to the clouds formed from the mist, the snow has started melting quickly. Apart from this the local crop patterns are affected. Post the 1990s, the Sutlej became a site for run of the river hydroelectric projects using extensive underground tunneling. This involves massive use of explosives for blasting through the mountains. Of the 23,000 MW worth of projects to be constructed in Himachal more than 10,000, a third are from this valley alone. Kinnaur continues to be a hydel powerhouse with 10 run of the river projects in progress and 30 more to be set up including two mega projects of 1500 MW and 1000 MW each. This paints a scary picture.
Interactive Sutlej River-Basin Map indicate Hydropower Station location
It is not just the hydro-electric dams but unplanned tourism and other development activities like mining, cement plants, road expansion and mindless construction across the high Himalayan regions have also add to the shift in local weather patterns, land use changes and thus the ecological crisis. But the reason why we should put the limelight on hydropower is that this is being pushed as “Green Energy”, in the name of climate change mitigation. As opposed to other forms of generating power, hydropower projects are said to cause lesser carbon emissions, which is why there has been a global push to shift to renewable resources. But the climate emergency in the Himalayas has put a question mark on ‘water’ as a renewable resource.
The question then arises that with all this data indicating a steady decline in river discharge and snow cover have our planners and policy makers not considered what will happen to these projects? Will they be able to generate the power they propose to? The people of Himalaya have to wake up to this wastage of public resources. Scarce funds should be diverted to better planning for securing local livelihoods by protecting the forest ecosystems and water sources for the future.
Author: Gagandeep Singh-From Himdhara (Environment Research and Action Collective)
Feature Images: unsplash/@raimondklavins
Environment
Chemical Waste Allegedly Poisons Ground Water in Solan Village, Killing Cattle and Causing Diseases in Villagers

Solan- The Shivalik Solid Waste Management Plant was set up at Village, Majra, Nalagarh, in District Solan 15 years ago. A no-objection certificate (NOC) was obtained from the Panchayat by telling it that it was an environment project. But, later, the villagers found that they were misled for obtaining this NOC. Only when this Plant was built, the villagers came to know that hazardous chemical solid toxic waste of the different factories of Himachal Pradesh was to be brought to this Solid Waste plant and that it was responsible for treating this solid waste.
When the cattle allegedly started dying and villagers fell ill due to various diseases, the villagers came to know that the Plant had contaminated the groundwater by dumping the waste into the ground instead of treating it.
A villager, Joginder Singh, Village Majra, alleged that villagers made many complaints to Pollution Control Board, as well as, various other higher authorities but till date, no action was been taken against the company.
He alleged that due to this poisonous water, their cattle have died and even the villagers have fallen victim to many serious diseases.
Eventually, Singh wrote a letter to the Chief Justice of the Himachal Pradesh High Court, in which it alleged that for the last 15 years, the aforesaid Plant was dumping the solid waste in the ground by covering it with soil, without proper treatment. Over time, the water of natural sources, wells and bore-wells of Panchayat Mazra and the surrounding villages became poisonous due to seepage of chemically contaminated water of this Plant into the ground and resultantly foul smell is emanating from the water.
He urged the Court to pass necessary directions for taking stringent action against the Shivalik solid Waste Management and save the villagers from the hazardous effect of this contaminated water.
A Division Bench comprising Acting Chief Justice Ravi Malimath and Justice Jyotsna Rewal Dua took suo moto cognizance of this letter, making it a Public Interest Litigation.
While hearing this petition, the HP High Court on September 27, 2021, issued a notice to the Chief Secretary, Member Secretary, H.P. State Environment Protection and Pollution Control Board, and the Deputy Commissioner, Solan, in a matter pertaining to the contamination of the water of Wells and Bore-Wells of the surrounding areas due to Chemical Waste of Shivalik Solid Waste Management Plant set.
The court posted the matter after two weeks and also directed the respondents to file their replies by the next date.
Environment
After 15 Years of Passing of Forest Rights Act, Implementation in Himachal Still in Doldrums, Jeopardizing Ecological Conservation

Shimla-‘Planting a tree to celebrate World Environment Day has been reduced to a symbolic tradition. But is this enough for the conservation of our ecology? The efficacy and use of plantation drives are being questioned all across the world today. These drives, especially when conducted by the government tend to be a wastage of resources due to poor survival rates, said environmental and community groups in Himachal Pradesh in a joint statement released recently on World Environment Day.
Further, trees are just one part of our ecosystem which comprises soil, grasslands, scrubs, wetlands, wildlife and even human beings, the statement said.
In India, especially in the Himalayas communities have co-existed with nature since times immemorial – dependent on it for day-to-day life and livelihoods, the groups said. Because of this connection between forests and local livelihoods and culture-communities across the landscape fought to protect the ecosystems they inhabit from destruction – be it the Chipko movement in Uttarakhand 50 years ago or the recent struggles in the tribal district of Kinnaur to highlight the ill-effects of dams and hydropower projects – indigenous and forest-dependent people have protected forest resources, they said.
“It is unfortunate then that these historical custodians of forests were labelled ‘encroachers’ and ‘thieves’ as their livelihoods were displaced from forests sometimes to build dams, highways and cities and at other times in the name of conservation were restricted from using the forests citing forest laws,” the statement said.
The groups said this has happened in Himachal too, where communities like pastoralists and farmers are slowly getting alienated from the forests. This jeopardizes their capacity to protect the forests too – whether from natural calamities like fires or indiscriminate felling.
Forest revival and afforestation programs, it is understood the world over, are only successful when local communities are made in charge and are given full access to use the forest and make decisions about its management.
“We have examples of community forest management like Gramya Jungles of Orissa and Van Panchayats of Uttarakhand. This became part of the Forest Policy in 1988 which is why programs like Joint Forest Management were planned for participatory governance of forests. However, in these too the forest department retained their control and communities were used as labour to plant trees,” the groups highlighted.
Based on these experiences and the repeated evictions of forest-dependent people from their rightful use it became apparent that there was a need for a law that recognised the community’s right to both use and protect/ govern the forest, they said.
It was after years of struggle that the Forest Rights Act 2006 was passed by the parliament of India. The Act recognises individual and community rights over any kind of forest lands for those dependent on these for their bonafide livelihood needs before 13th December 2005. The act also recognises development rights and community management rights. Himachal, where 2/3rd of the landscape is legally classified as ‘forest’ – there is a tremendous need and potential to implement this law to secure the land and livelihood rights of people on forest lands be they for fuelwood, fodder, pastures as well as farming and shelter.
The statement said today it has been 15 years since the passing of FRA but in Himachal, its implementation is in the doldrums.
“While 20 lakh forest rights claims have been accepted all across the country in Himachal only 164 claims have been recognised whereas 2700 are pending with the administration at various levels. The key reasons for the poor implementation include – lack of political will, misinformation about the act amongst the line officials, distrust of the people leading to non-filing of claims and inadequate awareness amongst common people,” the statement said.
It further said that, ironically, the state government has shown great enthusiasm in using this act to grant forest land for village development activities, the rest of the rights namely individual and community forest use and management rights are languishing due to state negligence and actively blocking the granting of these rights.
The groups further highlighted that in the last 5 years, community voices from Kangra, Chamba, Kinnaur, Lahaul-Spiti, Sirmaur and Mandi have been raising the demand for the implementation of this law in the state. It was after this that the state government was forced to announce that it would implement the Forest Rights Act in a mission mode in the state in 2018. The tribal department also worked on training and making educational material on the act. However, these are yet to be properly distributed at the village level.
The joint statement further added that in March 2020 post the pandemic led lockdown the FRA implementation process received a setback. Even as gram sabha meetings and FRC processes came to a grinding halt the economy too got hit. During this time, it became evident more than ever that it is the land and forest-based livelihoods that are available to rural communities to fall back on for survival.
“Whereas the Government should be focused on strengthening land and nature-based livelihoods for the local communities. However, the focus of the state remains on pushing destructive commercial ventures in ecologically fragile areas and valuable farmlands of the state,” the groups said.
The coronavirus has taught the world what the climate crisis had already indicated – that we will continue to be victims of such crisis as long as the ecological destruction continues unabated, the statement said.
“This calls for a change in the model of ‘development’ which prioritises the basic needs and services rather than run blindly after economic growth which is meant to profit companies and contractors”, the groups said.
The statement also said that it is the communities who will now have to believe in their own capacity to manage lives and resources and also call the government to account if our natural resources have to be protected for future generations.
Signatories
- Ajay Kumar, Sanjay Kumar, Advocate Dinesh, Bhoomiheen Bhoomi Adhikar Manch, Himachal
- Birbal Chaurhan, Shamlat Sangharsh Samiti, Sirmaur
- Gulab Singh and Dhaniram Shamra, Sirmaur Van Adhikar Manch
- Joginder Walia Balh Ghaati Kisaan Sangharsh Samiti, Mandi
- Jiya Negi, Van Adhikar Samiti, Kinnaur
- Kulbhushan Upmanyu, Himalaya Bachao Samiti, Chamba
- Lal Hussain, Ghumantu Pashupalak Mahasabha, Chamba
- Meera Devi, Nekram,Shyam Singh Chauhan, Paryavaran evam Gram Vikas Samiti, Karsog, Mandi
- Himshi Singh and Prakash Bhandari, Himdhara Environment Research and Action Collective
- Prem Katoch and Kesang Thakur, Save Lahaul Spiti, Lahaul
- Tenzin Takpa and Sonam Targey, Spiti Civil Society, Spiti
Image by OpenClipart-Vectors from Pixabay













 Home Decor Ideas 2020
Home Decor Ideas 2020
